Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT-THE D AND F BLOCK ELEMENTS-Exercise
- Write down the electronic configuration of: (i). Cr^(3+) (ii). Pm^...
Text Solution
|
- Why are Mn^(2+) compounds more stable than Fe^(2+) toward oxidation to...
Text Solution
|
- Explain briefly how +2 state become more and more stable in the first ...
Text Solution
|
- To what extent do the electronic configurations, decide the stability ...
Text Solution
|
- What may be the stable oxidation state of the transition element with ...
Text Solution
|
- Name the oxometal anions of the first series of the transition metals ...
Text Solution
|
- What is lanthanoid contraction? What are the consequences of lanthanol...
Text Solution
|
- What are the characteristics of the transition elements and why are th...
Text Solution
|
- In what way is the electronic configuration of the transition elements...
Text Solution
|
- What are the different oxidation states exhibited by the lanthanoids?
Text Solution
|
- Explain gives reason. (a) Transition metal and many of their compoun...
Text Solution
|
- What are interstitial compounds? Why are such compounds well known for...
Text Solution
|
- How is the variability in oxidation states of transition metals differ...
Text Solution
|
- Describe the preparation of potassium dichromate from iron chromite or...
Text Solution
|
- Describe the oxidising action of potassium dichromate and write the io...
Text Solution
|
- Describe the preparation of potassium permanganate. How does the acidi...
Text Solution
|
- For M^(2+)//M and M^(3+)//M^(2+) systems the E^(ϴ) values for some met...
Text Solution
|
- Predict which of the following will be coloured in aqueous solution? ...
Text Solution
|
- Compare the stability of +2 oxidation state for the elements of the fi...
Text Solution
|
- Compare the chemistry of actinoids with that of the lanthanoids with s...
Text Solution
|
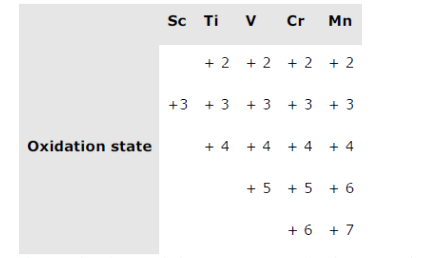 It can be easily observed that except Sc, all others metals display +2 oxidation state. Also, on moving from Sc to Mn, the atomic number increases from 21 to 25. This means the number of electrons in the 3d-orbital also increases from 1 to 5.
It can be easily observed that except Sc, all others metals display +2 oxidation state. Also, on moving from Sc to Mn, the atomic number increases from 21 to 25. This means the number of electrons in the 3d-orbital also increases from 1 to 5.