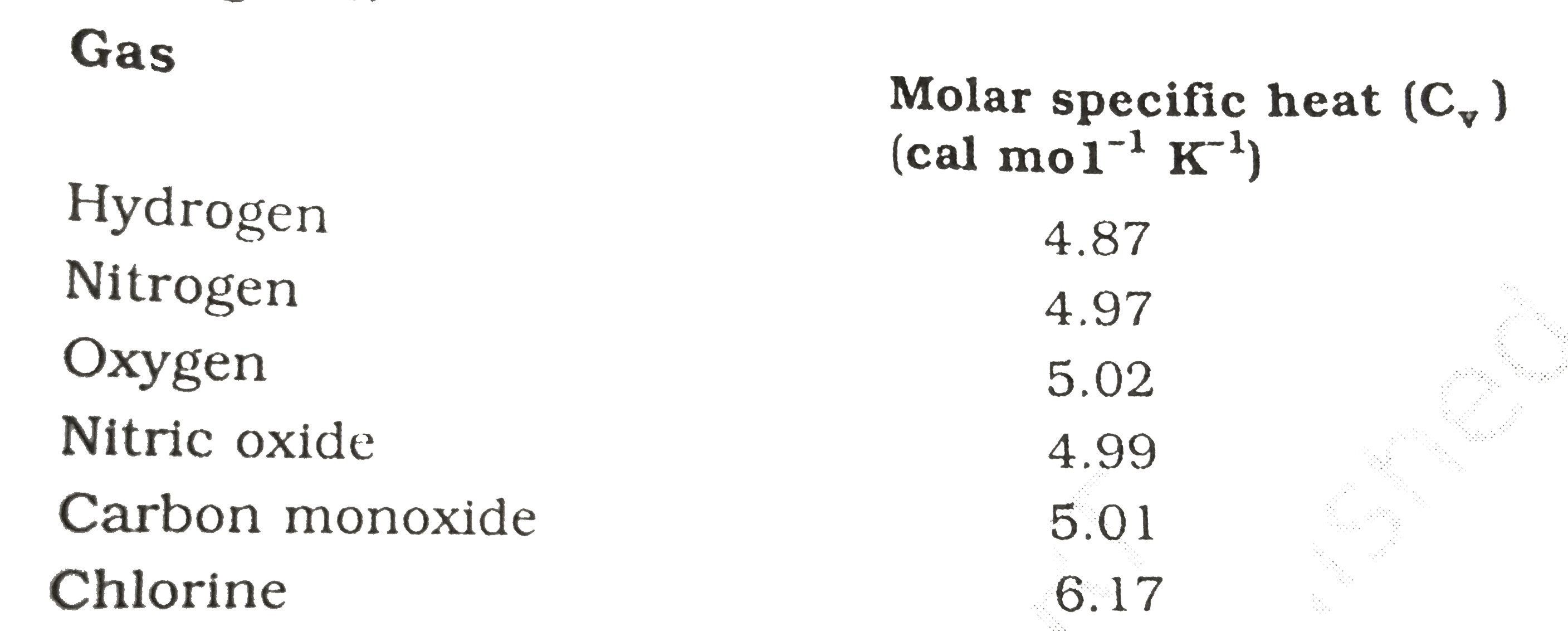Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT-THERMAL PROPERTIES OF MATTER-EXERCISE
- The electrical resistance in ohms of a certain thermometer varies with...
Text Solution
|
- Answer the following : (a) The triple-point of water is a standard...
Text Solution
|
- Two ideal gas thermometer A and B use oxygen and hydrogen respectively...
Text Solution
|
- A steel tape 1m long is correctly calibrated for a temperature of 27^(...
Text Solution
|
- a large steel wheel is to be fitted on to a shaft of the same material...
Text Solution
|
- A hole is drilled in a copper sheet. The diameter of the hole is 4.24 ...
Text Solution
|
- A brass wire 1.8 m long at 27^(@)C is held taut with little tension be...
Text Solution
|
- A brass rod of length 50 cm and diameter 3.0 cm is joined to a steel r...
Text Solution
|
- The coefficient of volume expansion of glycerine is 49 xx 10^(-5)//^(@...
Text Solution
|
- A 10 kW drilling machine is used to drill a bore in a small aluminium ...
Text Solution
|
- A copper block of mass 2.5 kg is heated in a furnace to a temperature ...
Text Solution
|
- In an experiment on the specific heat of a metal a 0.20 kg block of th...
Text Solution
|
- Given below are observations on molar specific heats at room temperatu...
Text Solution
|
- A child running a temperature of 101^F is given and antipyrin (i.e. a ...
Text Solution
|
- A thermocole cubical icebox of side 30 cm has a thickness of 5.0 cm if...
Text Solution
|
- A brass boiler has a base area of 0.15m^2 and thickness 1.0 cm it boil...
Text Solution
|
- Explain why : (a) A body with large reflectivity is a poor emitter. (...
Text Solution
|
- A body cools from 80^(@)C to 50^(@)C in 5 min-utes Calculate the time ...
Text Solution
|
- Answer the following questions based on the p-T phase diagram of carbo...
Text Solution
|
- Answer the following questions based on the P – T phase diagram of CO(...
Text Solution
|