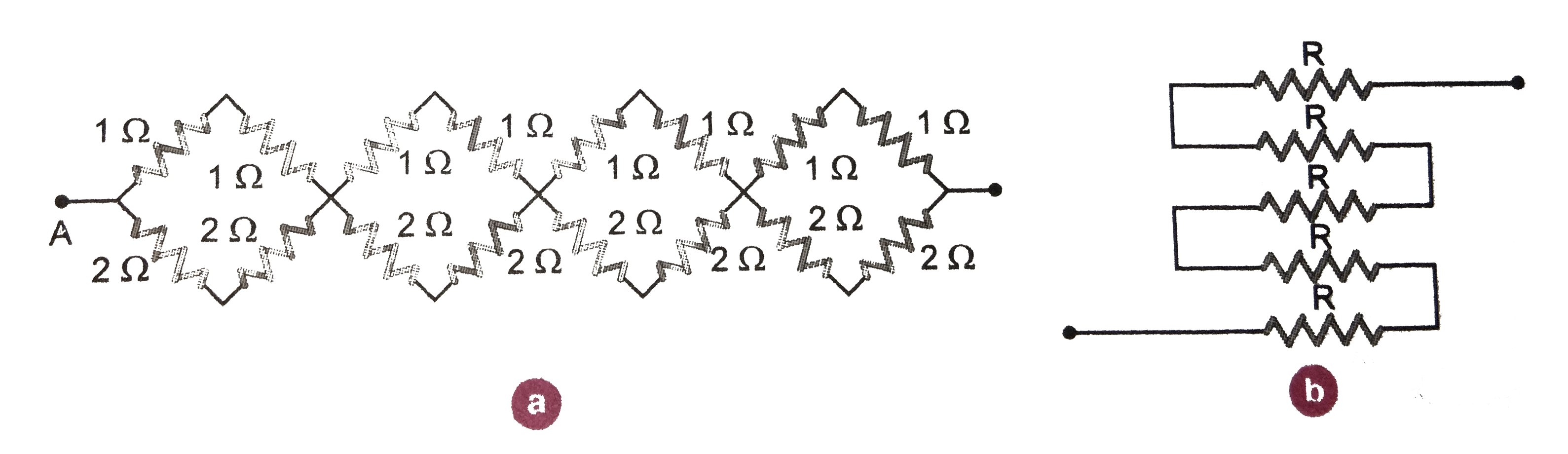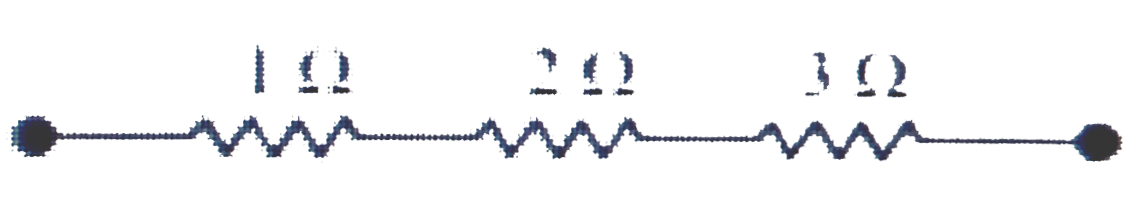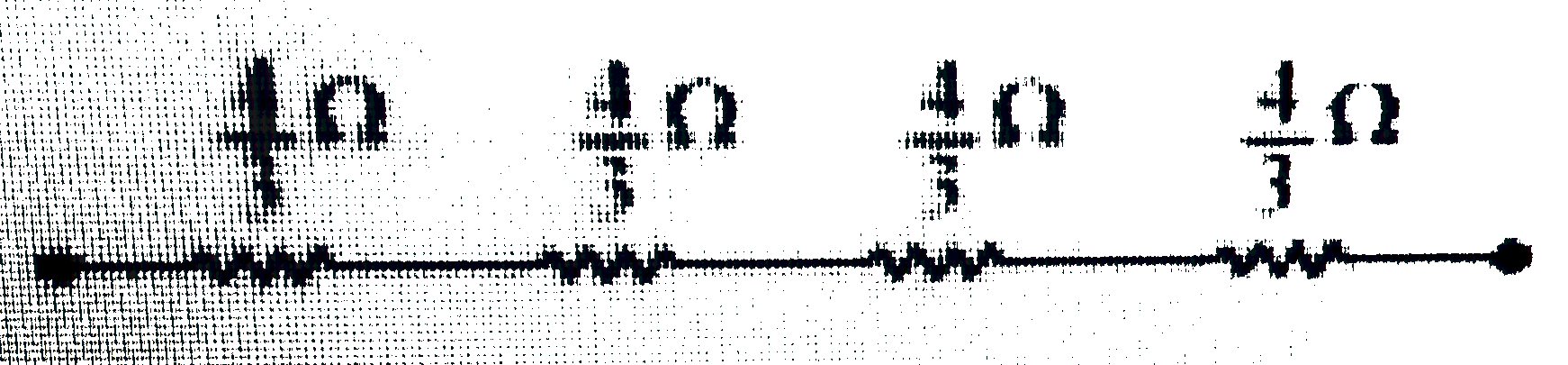(a) Total number of resistors = n
Resistance of each resistor = R
(i) When n resistors are connected in series, effective resistances `R_(1)` is the maximum given by the product nR
Hence, maximum resistance of the combination, `R_(1)=nR`
(ii) When n resistors are connected in parallel, the effective resistance `(R_(2))` is the minimum, given by ratio `(R)/(n)`
Hence, minium resistance of the combination, `R_(2)=(R)/(n)`
(iii) The ratio of the maximum to the minimum resistance is,
`(R_(1))/(R_(2))=(nR)/((R)/(n))=n^(2)`
(b) The resistance of the given resistors is,
`R_(1)=1 Omega, R_(2) = 2Omega, R_(3)=3 Omega2`
(i) Equilivalent resistance, `R=(11)/(3)Omega`
Consider the following combination of the resistors
Equilivalent resistance of the circuit is given by,
`R = (2xx1)/(2+1)+3=(2)/(3)+3=(11)/(3) Omega`
Equilivalent resistance of the circuit is given by,
`R = (2xx1)/(2+1)+3=(2)/(3)+3=(11)/(3) Omega`
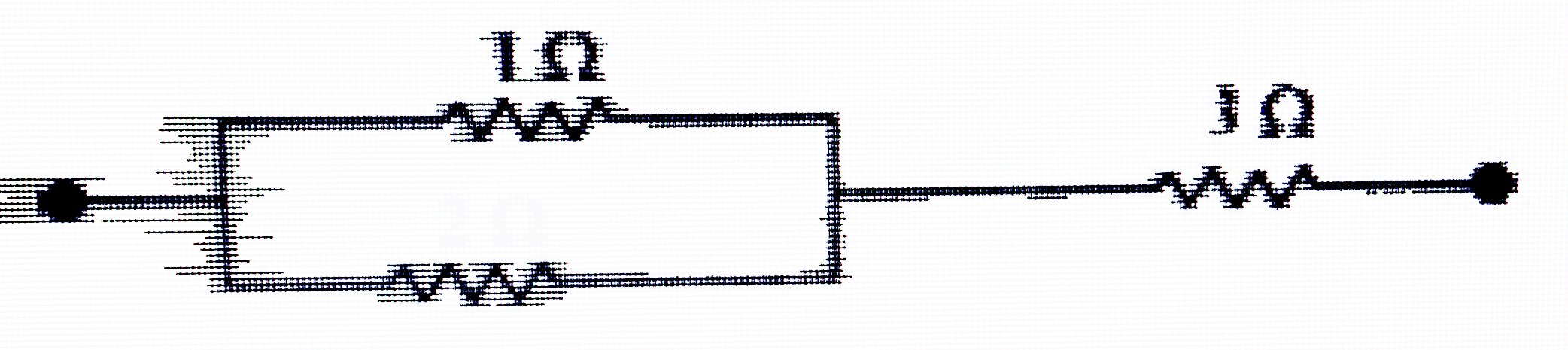
(ii) Equilivalent resistance, `R=(11)/(5) Omega`
Consider the following combination of the resistors

Equilvalent resistance of the circuit is given by,
`R' = (2xx3)/(2+3) +1=(6)/(5)+ 1=(11)/(5) Omega`
(iii) Equivalent resistance. `R = 6 Omega`
Consider the series combination of the resistor, as shown in the given circuit
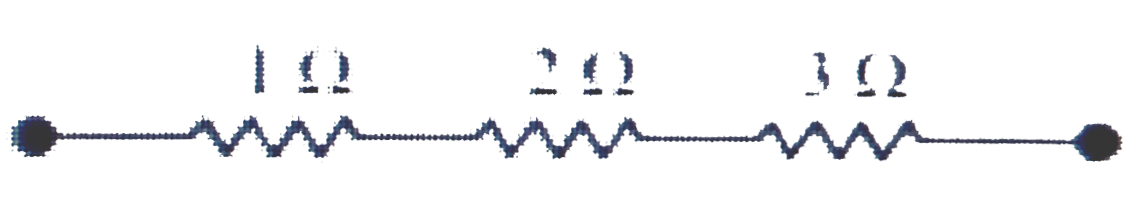
Equivalent resistane of the circuit is given by the sum,
`R = 1+2+3 = 6 Omega`
(iv) Equivalent resistance, `R = (6)/(11)Omega`
Consider the series combination of the resistors, as shown in the given circuit
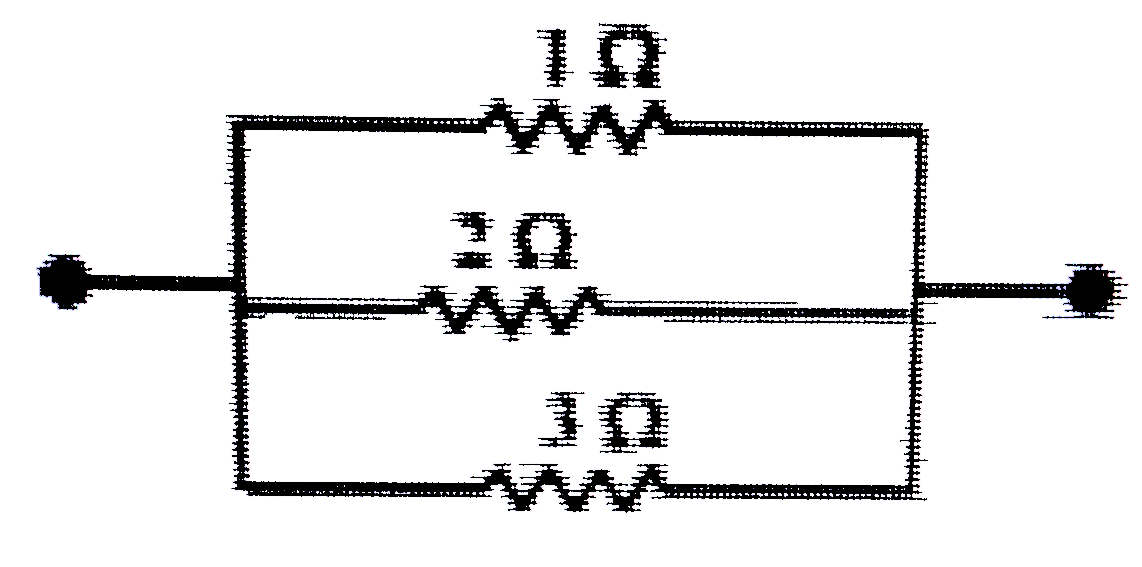
Equivalent resistance of the circuit is given by
`R = (1xx2xx3)/(1xx +2xx3 +3xx1)=(6)/(11) Omega`
(c) (a) It can be observed from the given that in the first small loop, two resistors of resistane `1 Omega` each are connected in series.
Hence, their equivalent resistance `= (1+1)=2 Omega`
It can also be observed that two resistors of resistance `2 Omega` each are connected in series. Hence, their equivalent resistance `= (2+2)=4 Omega`
Therefore, the circuit can be redrawn as

It can be observed that `2 Omega and 4 Omega` resistors are connected in parallel in all the four loops. Hence equivalent resistance (R) of each loop is given by
`R = (2xx4)/(2+4)=(8)/(6)=(4)/(3) Omega`
The circuit reduces to,
All the four resistors are connected in series.
Hence, equilvalent resistance of the given circuit is `(4)/(3) xx 4 = (16)/(3) Omega`
(b) It can be observed from the given circuit that five resistors of resistance R each are connected in series.
Hence, equivalent resistance of the circuit `= R+R+R+R+R = 5 R`.