Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT-ELECTRIC CHARGES AND FIELDS-EXERCISE
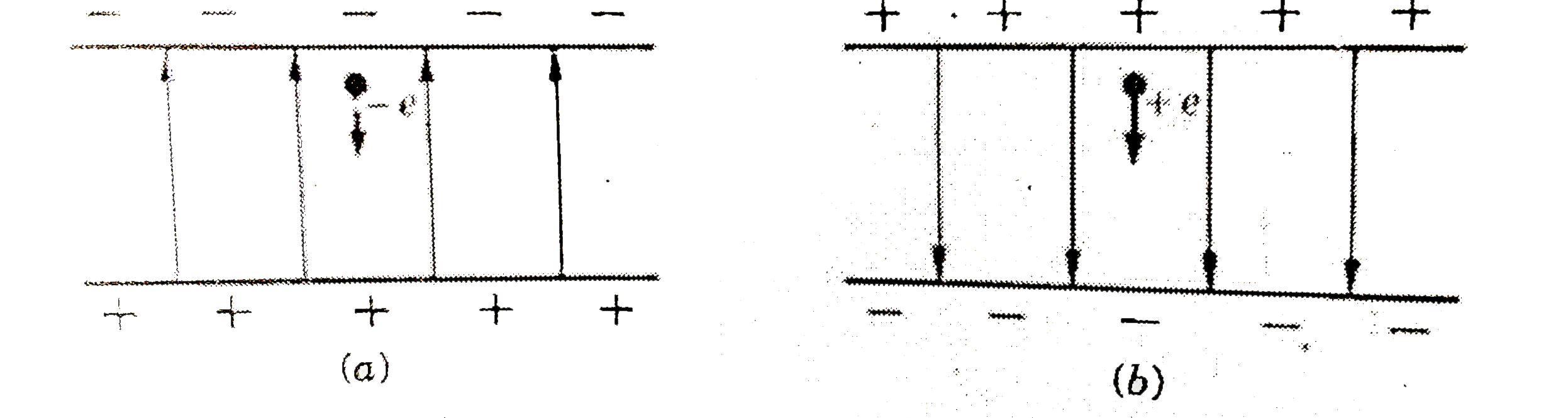
- An electron falls through a distance of 1.5 cm in a uniform electric f...
Text Solution
|
- What is the force between two small charged spheres having charges of...
Text Solution
|
- The electrostatic force on a small sphere of charge 0.4 muC due to ano...
Text Solution
|
- Check that the ratio ke2/G memp is dimensionless. Look up a Table of P...
Text Solution
|
- (a) Explain the meaning of the statement ‘electric charge of a body is...
Text Solution
|
- When a glass rod is rubbed with a silk cloth, charges appear on both. ...
Text Solution
|
- Four point charges q(A) = 2 mu C , q(B) = -5 mu C, q(C) = 2 mu C and ...
Text Solution
|
- (a) An electrostaic field line is a continous curve. That is a field l...
Text Solution
|
- Two point charges q(A) = 3 mu C and q(B) = -3 muC are located 20 cm ...
Text Solution
|
- A system has two charges q(A)= +2.5xx10^(-7)C and q(B)= -2.5xx10^(-7)C...
Text Solution
|
- An electrtic dipole with dipole moment 4xx10^(-9) C m is aligned at ...
Text Solution
|
- A polythene piece rubbed with wool is found to have a negative charge ...
Text Solution
|
- (a) Two insulated charged copper spheres A and B have their center...
Text Solution
|
- Suppose the spheres A and B in the above question have identical sizes...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows tracks of three charged particles crossing a uniform elec...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a uniform electric field E = 3xx10^(3) hat(i) N//C. (a) What...
Text Solution
|
- What is the net flux of the uniform electric field of the above questi...
Text Solution
|
- Careful measurement of the electric field at the surface of a black...
Text Solution
|
- A point charge +10 mu C is at distance of 5cm directly above the cente...
Text Solution
|
- A point charge of 2.0 muC is at center of a cublic Gaussian surface 9...
Text Solution
|
- A point charge causes an electric flux of -1.0xx10^(3) N m^(2)//C to p...
Text Solution
|