A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MOTION-CENTRE OF MASS-Exercise - 1
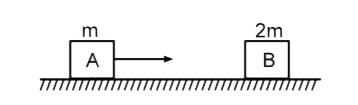
- In the figure shown the block A collides head on with another block B ...
Text Solution
|
- The centre of mass of two particles system lies
Text Solution
|
- A uniform square plate ABCD has a mass of 10kg. If two point masses of...
Text Solution
|
- There is a thin uniform disc of radius R and mass per unit area sigma,...
Text Solution
|
- In the adjacent diagram, objects 1 and 2 each have mass m while object...
Text Solution
|
- Four particles of mass 5,3,2,4 kg are at the points (1,6),(-1,5),(2,-3...
Text Solution
|
- As shown in diagram there are five identical rods. Length of each rod ...
Text Solution
|
- The position vectors of three particles of mass m(1) = 1kg, m(2) = 2kg...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows a uniform disc of radius R, from which a hole of radius R...
Text Solution
|
- Find the centre of mass of a uniform L shaped lamina (a thin flat plat...
Text Solution
|
- A graph between kinetic energy and momentum of a particle is plotted a...
Text Solution
|
- A Wireframe is made of a wire or uniform crosssection. which is shown ...
Text Solution
|
- Look at the drawing given in the figure which has been drawn with ink ...
Text Solution
|
- A man of mass M stands at one end of a stationary plank of length L, l...
Text Solution
|
- Two balls A and B of masses 100gm and 250 gm respectively are connecte...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass 3m is projected from the ground at some angle with ...
Text Solution
|
- A man weighing 80 kg is standing at the centre of a flat boat and he i...
Text Solution
|
- Two particles having mass ratio n:1 are interconnected by a light inex...
Text Solution
|
- Internal forces can change
Text Solution
|
- A small sphere is moving at a constant speed in a vertical circle. Bel...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following graphs represents the graphical relation betwee...
Text Solution
|