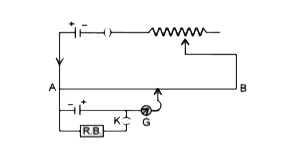
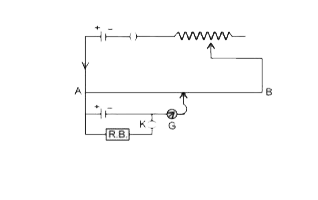
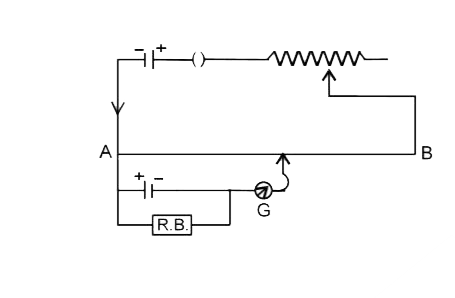
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Electrical Instrument
MOTION|Exercise EXERCISE -2|21 VideosElectrical Instrument
MOTION|Exercise EXERCISE -3|16 VideosElectrical Instrument
MOTION|Exercise EXERCISE -3|16 VideosELASTICITY AND THERMAL EXPANSION
MOTION|Exercise Exercise - 4 (Level-II)|11 VideosELECTRO MAGNETIC INDUCTION
MOTION|Exercise EXERCISE-4| Section B (Prevous Years Problems )|29 Videos
MOTION-Electrical Instrument -EXERCISE -1
- Potentiometer is an ideal instrument because
Text Solution
|
- A potentiometer works on the principle that
Text Solution
|
- If the length of potentiometer wire is increased, then the accuracy in...
Text Solution
|
- In an ammeter calibration experiment, the potentiometer is used to mea...
Text Solution
|
- In potentiometer the potential gradient is –
Text Solution
|
- If the potentiometer wire having resistance rho ohm/ m and I amp. curr...
Text Solution
|
- Discuss the principle of potentiometer and explain the determination o...
Text Solution
|
- The material of wire of potentiometer is
Text Solution
|
- If the current in the primary circuit of a potentiometer wire of speci...
Text Solution
|
- The p.d. between A and B is balanced at 2.036 m length of the potentio...
Text Solution
|
- In the following figure, the p.d. between the points M and N is balanc...
Text Solution
|
- In the foregoing question, the balancing length between the p.d. betwe...
Text Solution
|
- In a potentiometer of one meter length , an unknown emf voltage source...
Text Solution
|
- The voltage across the two equal resistances connected in series get b...
Text Solution
|
- The quantity that cannot be measured by a potentiometer is….
Text Solution
|
- Correct diagram for the determination of internal resistance of a prim...
Text Solution
|
- A potentiometer has uniform potential gradient across it. Two cells c...
Text Solution
|
- A wire connected in the left gap of a meter bridge balance a 10Omega r...
Text Solution
|
- With two resistance R1 and R2 (>R1) in the two gaps of a metre bridge ...
Text Solution
|
- In a simple meter bridge circuit, the gaps are bridged by cord P and Q...
Text Solution
|