Which of the following si most reactive toward `S_(N^(2))` reaction ?
Which of the following si most reactive toward `S_(N^(2))` reaction ?
A
`CH_(2)=CH-CH_(2)-Cl`
B
`Ph-CH_(2)-Cl`
C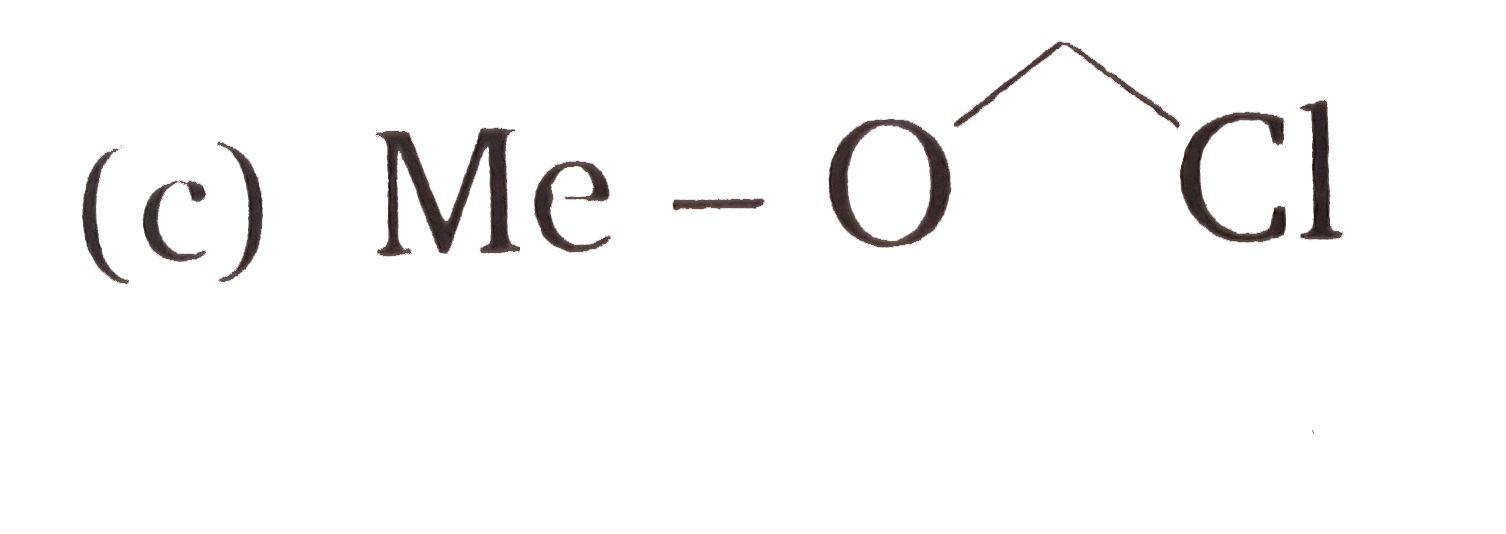
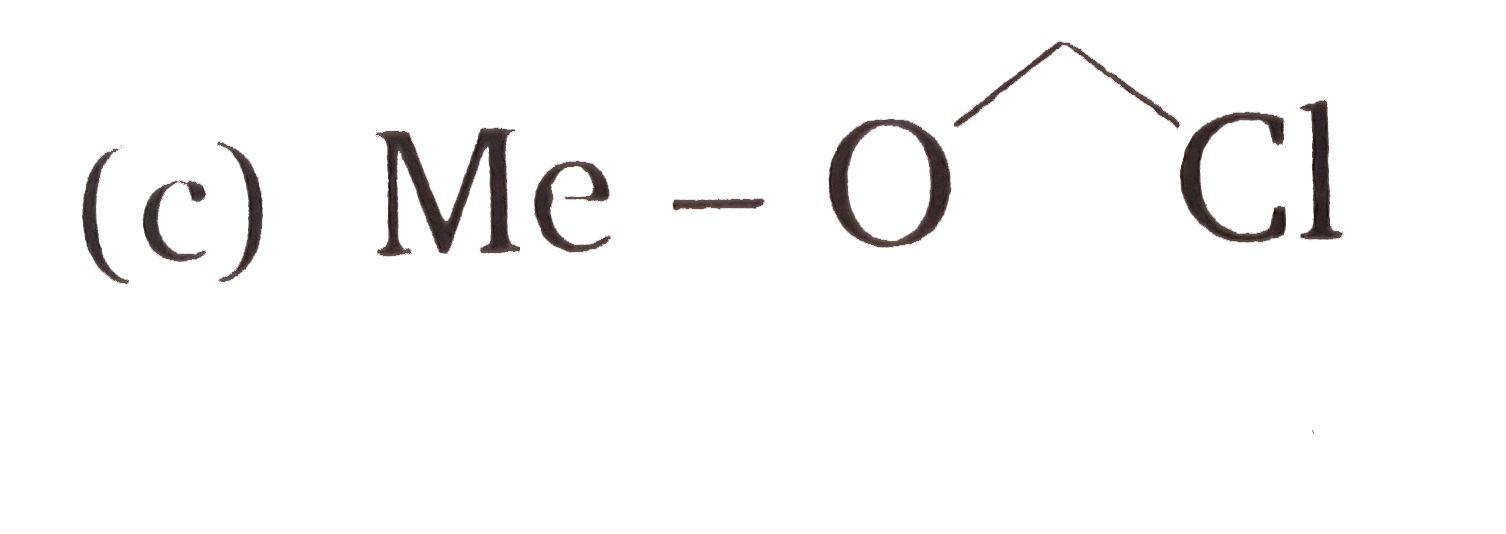
D
`Ph-underset(O)underset(||)C-CH_(2)-Cl`
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
To determine which of the given compounds is most reactive toward an \( S_N2 \) reaction, we need to analyze the structure of each compound and consider factors that affect \( S_N2 \) reactivity, such as steric hindrance, the nature of the leaving group, and the ability of the nucleophile to attack the electrophile.
### Step-by-Step Solution:
1. **Identify the Compounds**:
Let's denote the four compounds as A, B, C, and D. We need to assess their structures and the substituents attached to the carbon that is undergoing substitution.
2. **Evaluate Steric Hindrance**:
\( S_N2 \) reactions involve a backside attack by the nucleophile on the carbon atom attached to the leaving group. Therefore, steric hindrance plays a crucial role. Primary carbons are more reactive than secondary, and tertiary carbons are the least reactive due to steric hindrance.
3. **Analyze the Leaving Group**:
The ability of the leaving group to depart is also critical. A good leaving group (like \( Cl^- \), \( Br^- \), or \( I^- \)) will enhance the reactivity of the substrate. If all compounds have the same leaving group, we can focus on sterics and nucleophilicity.
4. **Consider Resonance Effects**:
If any of the compounds have substituents that can stabilize the transition state through resonance, this can also increase the reactivity. For example, if a compound has a phenyl group or another electron-withdrawing group, it may stabilize the transition state.
5. **Compare the Compounds**:
- **Compound A**: If it has a primary carbon with a good leaving group, it will be very reactive.
- **Compound B**: If it has a benzene ring, the resonance may stabilize the transition state but also create steric hindrance.
- **Compound C**: If it has an oxygen atom or another electronegative atom, it could stabilize the transition state but also create steric hindrance.
- **Compound D**: If it has a tertiary carbon, it will be the least reactive due to steric hindrance.
6. **Determine the Most Reactive Compound**:
After analyzing the steric hindrance and resonance effects, the compound with the least steric hindrance and a good leaving group will be the most reactive toward \( S_N2 \) reactions.
### Conclusion:
Based on the analysis, the compound that has a primary carbon with a good leaving group will be the most reactive toward \( S_N2 \) reactions.
---
To determine which of the given compounds is most reactive toward an \( S_N2 \) reaction, we need to analyze the structure of each compound and consider factors that affect \( S_N2 \) reactivity, such as steric hindrance, the nature of the leaving group, and the ability of the nucleophile to attack the electrophile.
### Step-by-Step Solution:
1. **Identify the Compounds**:
Let's denote the four compounds as A, B, C, and D. We need to assess their structures and the substituents attached to the carbon that is undergoing substitution.
2. **Evaluate Steric Hindrance**:
...
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Which of the foollowing is most reactive toward S_(N^(2)) reaction ?
Which of the following is most reactive toward SNAr :
Which of the following is most reactive towards S_(N)1 reaction?
Which of the following is most reactive towards H_2 ?
Which of the following is most reactive towards S_(N)2 reaction? CH_(3)Br, (CH_(3))_(2)CHBr, (CH_(3))_(3)CBr
Which of the following is most reactive towards S_(N)2 reaction? CH_(3)Br, (CH_(3))_(2)CHBr, (CH_(3))_(3)CBr