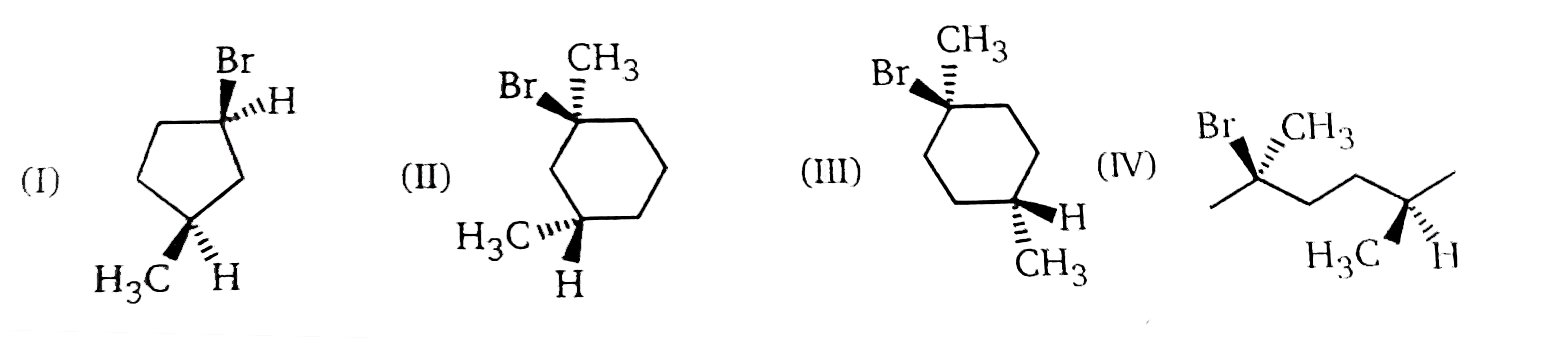
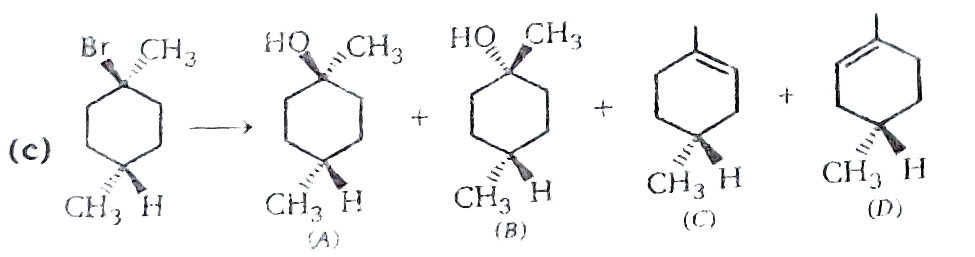Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Under the specifed condition s ,subastan e X undergoes subition ans el...
Text Solution
|
- State whether the following statements are true or false. a. D and L...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the compound (A) given below: a. Give the total number of ste...
Text Solution
|
- Under the specifed condition s ,subastan e X undergoes subition ans el...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following complexes will give a pair of enantiomers ?
Text Solution
|
- Name the enantiomer of alpha-D-(+)-glucose.
Text Solution
|
- Determine if the following pairs are identical, isomers, enantiomers, ...
Text Solution
|
- মনে করো, A = {a, b, c, d, e,j, g, h, i}, B = {b, d,f, h},C = {a, c, e,...
Text Solution
|
- মনে করো, A = {a, b, c, d, e,j, g, h, i}, B = {b, d,f, h},C = {a, c, e,...
Text Solution
|