Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MOTION-WORK, POWER & ENERGY -SOLVED EXAMPLES
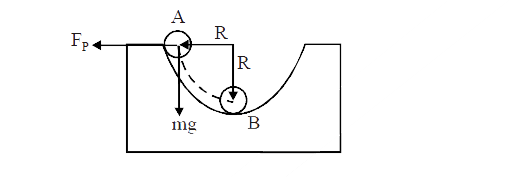
- Figure shows two block A and B, each having a mass of 320 g connected ...
Text Solution
|
- A small disc A slides down with initial velocity equal to zero from th...
Text Solution
|
- A constant horizontal force F of magnitude equal to (mg)/(2) begins to...
Text Solution
|
- A small body is placed at rest at the bottom B of a smooth hemispheric...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is suspended vertically from a point O by an inextensible m...
Text Solution
|