A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
GASEOUS STATE
MOTION|Exercise EXERCISE -1 (INTRODUCTION & STATE PARAMETERS)|44 VideosGASEOUS STATE
MOTION|Exercise EXERCISE-2(LEVEL-I)|48 VideosGASEOUS STATE
MOTION|Exercise SOLVED EXAMPLE|15 VideosELECTROCHEMISTRY
MOTION|Exercise EXERCISE-4,II|44 VideosGOC
MOTION|Exercise Exercise - 4 Level - II|14 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MOTION-GASEOUS STATE -SOLVED EXAMPLE(IIT-JEE MAINS)
- Calculate the density of NH(3) at 30^(@)C and 5 atm pressure.
Text Solution
|
- 3 moles of a gas are present in a vessel at a temperature of 27^(@)C ....
Text Solution
|
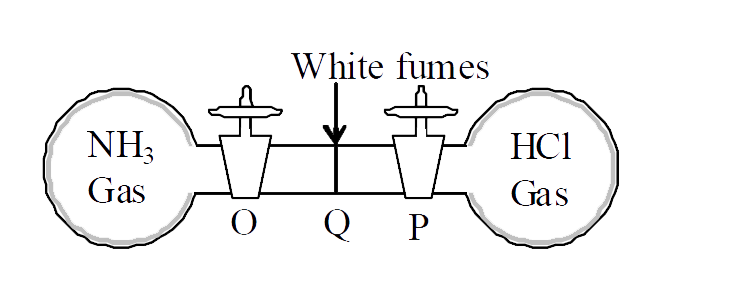
- In the following diagram,container of NH(3) gas and container of HCl g...
Text Solution
|
- The root mean square speed of hydrogen is sqrt(5) times than that of n...
Text Solution
|
- A jar contains a gas and a few drops of water at TK The pressure in th...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate relative rate of effusion of O(2) to CH(4) from a container ...
Text Solution
|
- At what temperature will average speed of the molecules of the second...
Text Solution
|
- 80 mL of O(2) takes 2 minutes to pass through the hole. What volume of...
Text Solution
|
- The density of a gas filled in electric lamp is 0.75kg//m^(3) . After ...
Text Solution
|
- If one mole each of a monoatomic and diatomic gases are mixed at low t...
Text Solution
|
- If one mole of a monatomic gas (gamma=5/3) is mixed with one mole of a...
Text Solution
|
- The average speed at temperature T^(@)C of CH(4)(g) is sqrt((28)/(88))...
Text Solution
|
- The intercept on y-axis and slope of curve plotted between P/T vs. T ...
Text Solution
|
- Two vessels connected by a valve of negligible volume. One container (...
Text Solution
|
- Two closed vessels of equal volume containing air at pressure P(1) and...
Text Solution
|
- 7 moles of a tetra-atomic non-linear gas 'A' at 10 atm and T K are mi...
Text Solution
|
- A balloon of diameter 21 meter weight 100 kg. Calculate its pay-load, ...
Text Solution
|
- The density of vapour of a substance (X) at 1 atm pressure and 500 K ...
Text Solution
|
- A given volume of ozonised oxygen (containing 60% oxygen by volume ) r...
Text Solution
|
- For a real gas (mol.mass =60) if density at critical point is 0.80g//c...
Text Solution
|