Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
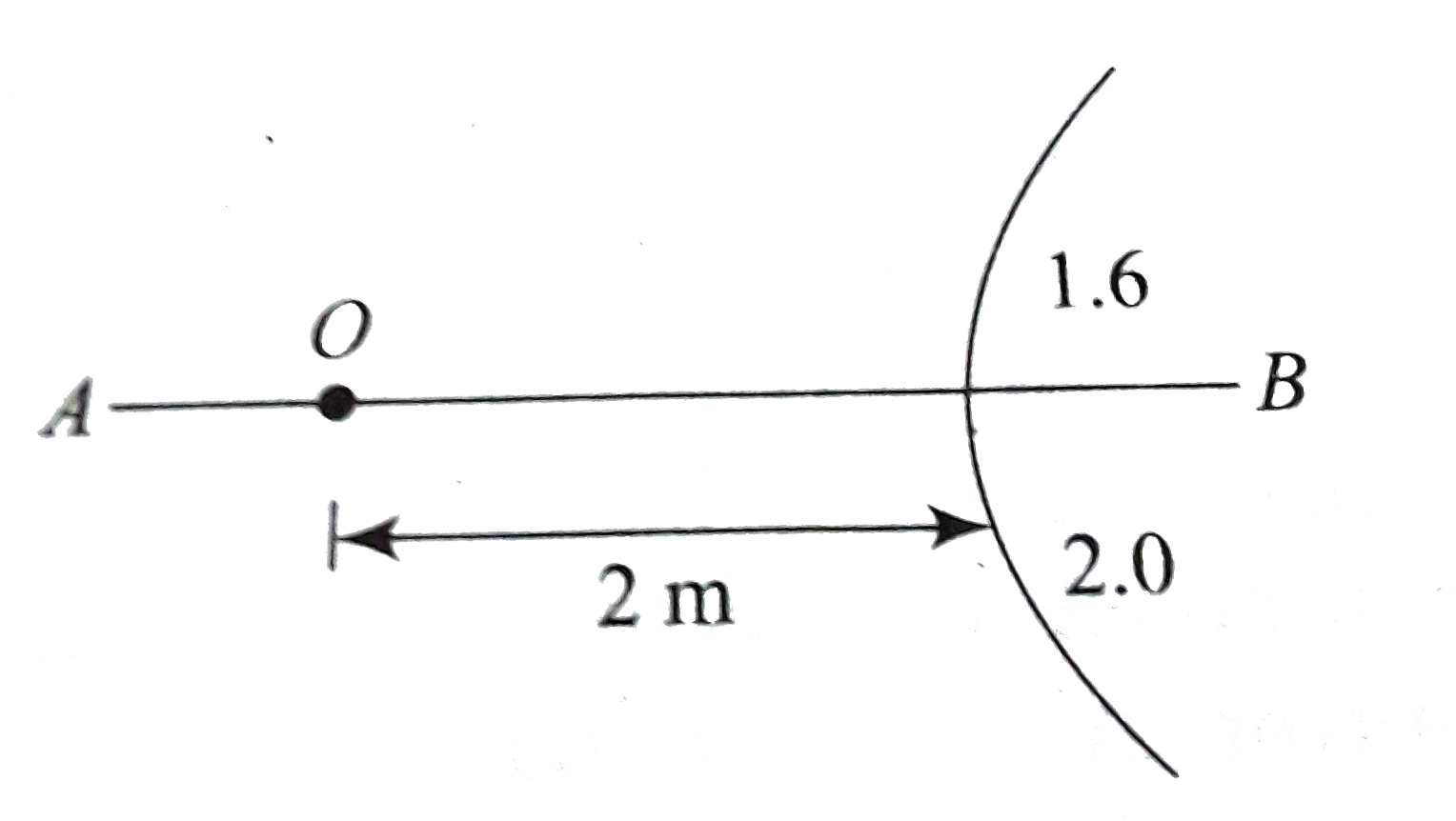
- In Figure, a point object O is placed in air. A spherical boundary sep...
Text Solution
|
- Two refracting media are separated by a spherical interfaces as shown ...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure, a point object O is placed in air. A spherical boundry ...
Text Solution
|
- Refraction takes place at a convex spherical boundary separating glass...
Text Solution
|
- In Figure, a point object O is placed in air. A spherical boundary sep...
Text Solution
|
- A concave spherical refractive surface with radius R separates a mediu...
Text Solution
|
- Refraction takes place at a concave spherical boundary separating glas...
Text Solution
|
- Two refracting media are separated by a spherical interface as shown i...
Text Solution
|
- The diagram shows a spherical surface which separates two media of ref...
Text Solution
|