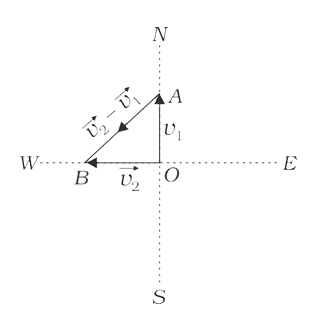
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A car travelling at a speed of 30 ms^(-1) due north along the highway ...
Text Solution
|
- A car is moving on a straight road due north with a uniform speed of 5...
Text Solution
|
- A car travelling at a speed of 30 ms^(-1) due north along the highway ...
Text Solution
|
- A car travels due east on a level road for 30 km. It then turns due no...
Text Solution
|
- A car travelling a 20 ms^(-1) due north along the highway makes a righ...
Text Solution
|
- What is the maximum speed at which a car can turn round a curve of 30 ...
Text Solution
|
- A car travels from rest with a constant acceleration "a" for "t" secon...
Text Solution
|
- A car travels from rest with a constant acceleration 'a' for 't' secon...
Text Solution
|
- A car travels from rest with a constant acceleration 'a' for 't' secon...
Text Solution
|