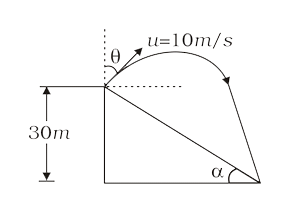
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A ball is thrown upwards from the top of an incline with angle of proj...
Text Solution
|
- A ball projected upwards from the foot of a tower. The ball crosses th...
Text Solution
|
- On an inclined plane of inclination 30^(@) , a ball is thrown at angle...
Text Solution
|
- A ball is projected perpendicularly from an inclined plane of angle th...
Text Solution
|
- A ball is projected from a cliff of height h = 19.2 m at an angle a to...
Text Solution
|
- A ball is thrown upwards from the top of an incline with angle of proj...
Text Solution
|
- A ball is thrown upwards from the top of an incline with angle of proj...
Text Solution
|
- A ball is projected from top of the table with initial speed u at an a...
Text Solution
|
- A ball is throuwn with a speed of 20 m//s from top of a buling 150 m h...
Text Solution
|