Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
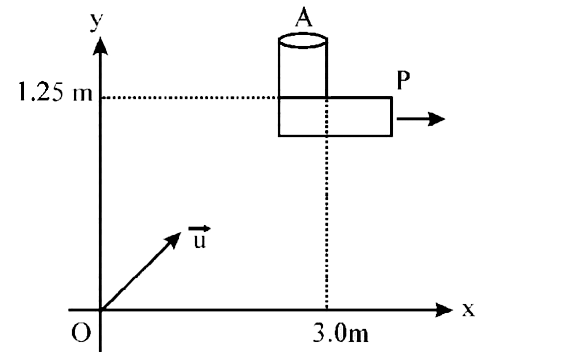
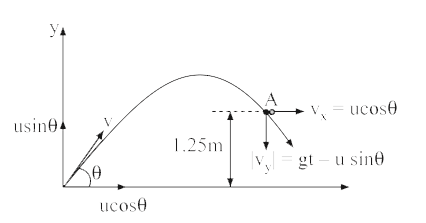
- An object A is kept fixed at the point x= 3 m and y = 1.25 m on a pl...
Text Solution
|
- An object A is kept fixed at the point x= 3 m and y = 1.25 m on a pl...
Text Solution
|
- Acceleration of a particle in x-y plane varies with time as a=(2t hati...
Text Solution
|
- A man of mass m is moving with a constant acceleration a w.r.t plank i...
Text Solution
|
- A stone is projected from level ground at t=0 sec such that its horizo...
Text Solution
|
- A block is moving along y-axis with velocity vec(v)(A)=4hat(j) on a pl...
Text Solution
|
- An object at rest at the origin begins to move in the +x direction wit...
Text Solution
|
- भूमि से ऊपर उठे किसी तख्ते P पर बिंदु x =3 मी तथा y=1.25 मी पर एक वस्त...
Text Solution
|
- A Body start from origin and move along x-axis such that velocity at a...
Text Solution
|