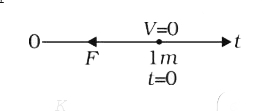
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A particle of mass 10^-2kg is moving along the positive x axis under t...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass 10^-2kg is moving along the positive x axis under t...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is moving along x-axis. At time t=0, Its x-coordinate is x=...
Text Solution
|
- Velocity (in m/s) of a particle moving along x-axis varies with time a...
Text Solution
|
- The displacement to particle is zero at t=0 and is z at t= t. It star...
Text Solution
|
- The dispkacement of particle is zero at t= 0 and it is x , at t-t . It...
Text Solution
|
- A particle constrained to move along the x-axis in a potential V=k"...
Text Solution
|
- A body of mass m, moving along the positive x direction is subjected t...
Text Solution
|
- The position (x) of a particle of mass 2 kg moving along x-axis at tim...
Text Solution
|