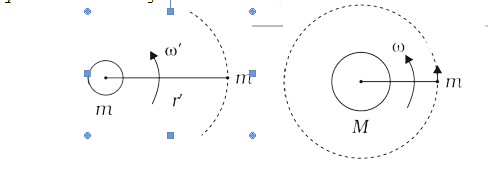
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A satellite can be in a geostationary orbit around earth in an orbit o...
Text Solution
|
- For a geostationary satellite orbiting around the earth identify the n...
Text Solution
|
- A satellite can be in a geostationary orbit around earth in an orbit o...
Text Solution
|
- The height of geostationary orbit above the surface of the earth is h....
Text Solution
|
- A satellite can be in a geostationary orbit around earth at a distance...
Text Solution
|
- If mean radius of earth is R, its angular velocity is omega and the ac...
Text Solution
|
- A satellite is orbiting around the earth at a mean radius of 16 times ...
Text Solution
|
- Radius of a geostationary satellite revolving round the earth is 'r'. ...
Text Solution
|
- पृथ्वी के भू-स्थिर उपग्रह की कक्षा की त्रिज्या कितनी होती है ?
Text Solution
|