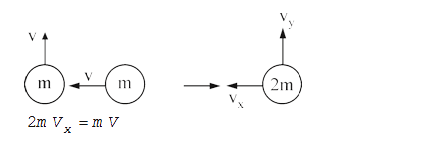
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A satellite of mass M is in a circular orbit of radius R about the cen...
Text Solution
|
- Consider two satellites A and B of equal mass m , moving in the same c...
Text Solution
|
- Two satellite of same mass are launched in the same orbit of radius r ...
Text Solution
|
- A satellite is revolving around earth in a circular orbit at a height ...
Text Solution
|
- An artifical satellite of mass m travels at a constant speed in a circ...
Text Solution
|
- A satellite of mass M is in a circular orbit of radius R about the cen...
Text Solution
|
- m द्रव्यमान का एक उपग्रह पृथ्वी ( द्रव्यमान M ) के चारों ओर r त्रिज्या...
Text Solution
|
- A satellite X moves round the earth in a circular orbit of radius R . ...
Text Solution
|
- M द्रव्यमान का एक उपग्रह पृथ्वी के परितः R त्रिज्या की एक वृत्तीय कक्ष...
Text Solution
|