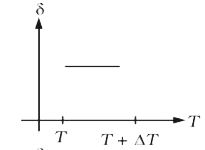
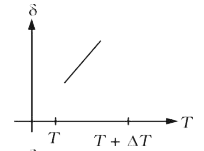
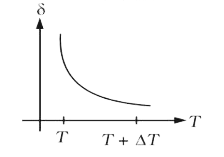
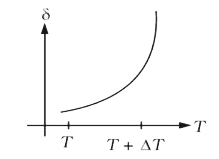
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- An ideal gas is initially at temperature T and volume V. Its volume is...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal gas is initially at temperature T and volume V. Its volume is...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal gas is initially at temperature T and volume V . Its volume i...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal gas is initially at temperature T and volume V. Its volume is...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal gas is initiaily at temperature T and volumoeV. lts volume is...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal gas is initially at temperature T and volume V. Its volume is...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal gas is initially at temperature T and volume V. Its volume is...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal gas is initially at temperature T and volume V. ITS volume is...
Text Solution
|
- एक आदर्श गैस प्रारम्भ में तापमान T और आयतन V पर होती है। इसके तापमान म...
Text Solution
|