Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
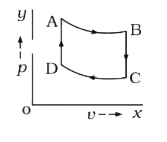
- One mole of a monatomic ideal gas is taken through the cycle shown in ...
Text Solution
|
- The value of (Cp - Cv) is 1.00 R for a gas sample in state A and is ...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of a monoatomic ideal gas is taken through the cycle shown in...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of a monoatomic ideal gas is taken through the cycle shown in...
Text Solution
|
- On mole of a monoatomic ideal gas is taken through the cycle shown in ...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of a monatomic ideal gas is taken through the cycle shown in ...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of a monatomic ideal gas is taken through the cycle shown in ...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of a monatomic ideal gas is taken through the cycle shown in ...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of a monatomic ideal gas is taken through the cycle shown in ...
Text Solution
|