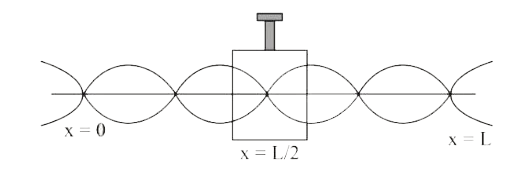Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Recommended Questions
- A metallic rod of length 1m is rigidly clamped at its mid point. Longi...
Text Solution
|
- A steel rod 2.5 m long is rigidly clamped at its centre C and longitud...
Text Solution
|
- A metallic rod of length 1m has one end free and other end rigidly cla...
Text Solution
|
- A metallic rod of length 1m has one end free and other end rigidly cla...
Text Solution
|
- A metallic rod of length 1m has one end free and other end rigidly cla...
Text Solution
|
- A metallic rod of length 1m is rigidly clamped at its mid point. Longi...
Text Solution
|
- A metallic rod of length 1m is rigidly clamped at its end points. Long...
Text Solution
|
- A metallic rod of length 1m is rigidly clamped at its midpoint. Longi...
Text Solution
|
- 1 मी लम्बी धातु की छड़ को उसके मध्य - बिन्दु पर दृढ़तापूर्वक कसा गया है...
Text Solution
|