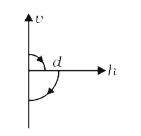
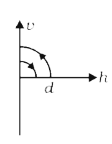
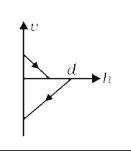
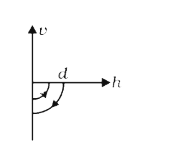
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A ball is dropped vertically from a height d above the ground . It hit...
Text Solution
|
- A ball is dropped vertically from a height d above the ground . It hit...
Text Solution
|
- A ball is dropped vertically from a height d above the ground. It hits...
Text Solution
|
- A ball is dropped from a height h above ground. Neglect the air resist...
Text Solution
|
- 7. A ball is dropped vertically from a height d above the ground. It h...
Text Solution
|
- A ball is dropped vertically from a height above the ground. It hits t...
Text Solution
|
- A ball is dropped vertically from a height above the ground. It hits t...
Text Solution
|
- A ball is dropped vertically, from a height h above the ground. It hit...
Text Solution
|
- A ball is dropped vertically from a height h above the ground .It hits...
Text Solution
|