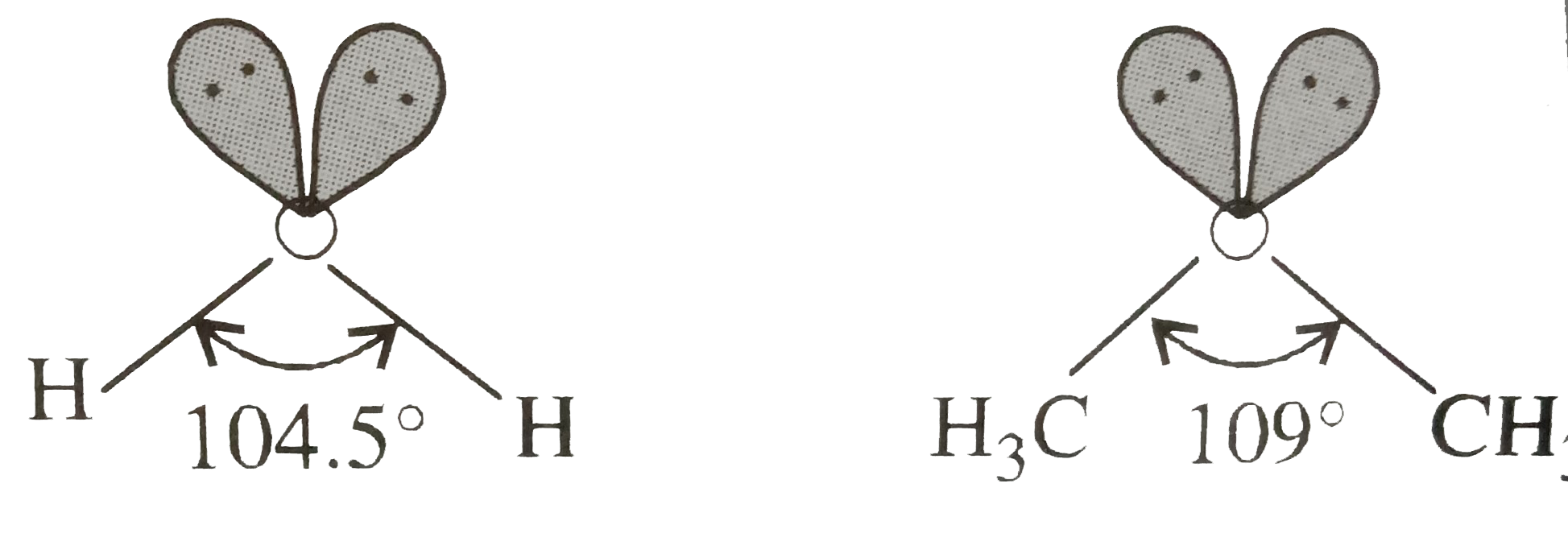Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
CHEMICAL BONDING AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE
DINESH PUBLICATION|Exercise ADDITIONAL IMPORTANT QUASTIONS|41 VideosCHEMICAL BONDING AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE
DINESH PUBLICATION|Exercise H.O.T.S. CONCEPTUAL QUESTIONS|11 VideosCHEMICAL BONDING AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE
DINESH PUBLICATION|Exercise COMPREHENSION|4 VideosCARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND THEIR DERIVATIVES
DINESH PUBLICATION|Exercise Unit test|20 VideosCLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS AND PERIODICITY IN PROPERTIES
DINESH PUBLICATION|Exercise All Questions|310 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DINESH PUBLICATION-CHEMICAL BONDING AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE -BORD EXAMINATIONS
- Why does type of overlap given in the following figure not result in b...
Text Solution
|
- Explain why PCl(5) is trigonal bipyramidal whereas IF(5) is square pyr...
Text Solution
|
- In both water and dimethyl ether (CH(3)-underset(* *)overset(* *)O-CH...
Text Solution
|
- The energy of sigma2p(z), molecular orbital is greater than pi2p(x) an...
Text Solution
|
- Give the change in bond order in the following ionisation process? i...
Text Solution
|
- Give reasons for the following : (i) Covalent bonds are directional...
Text Solution
|
- What is an ionic bond ? With two suitable examples, explain the difere...
Text Solution
|
- Explain why CO(3)^(2-) ion cannot be represented by a single Lewis str...
Text Solution
|
- Predict the hybridisation of each carbon in the molecule of organic co...
Text Solution
|
- Group the following as linear and non-linear molecules : H(2)O,HOCl,...
Text Solution
|
- Elements X,Y and Z have 4,5 and 7 valence electrons respectively, (i) ...
Text Solution
|
- Draw the resonatin structure of (i) Ozone molecule (ii) Nitrate ion
Text Solution
|
- Presict the shapes of the following molecules on the basis of hybridis...
Text Solution
|
- All the C-O bonds in carbonate in (CO(3)^(2-)) are equal in length. Ex...
Text Solution
|
- What is meant by the term vaerange bond enthalpy? Why is there differe...
Text Solution
|
- (I) Discuss the significance/applications of dipole moment. (ii) Rep...
Text Solution
|
- Use the molecular orbital energy level diagram to show that N(2) would...
Text Solution
|
- Briefly describe the valence bond theory of covalent bond formation by...
Text Solution
|
- Describe hybridisation in the case of PCl(5) and SF(6) The axial bonds...
Text Solution
|
- Discuss the concept of hybridisation. What are its different types in ...
Text Solution
|