Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
STATES OF MATTER : GASES AND LIQUIDS
DINESH PUBLICATION|Exercise Concept Based Questions|32 VideosSTATES OF MATTER : GASES AND LIQUIDS
DINESH PUBLICATION|Exercise Additional Important Questions|22 VideosSTATES OF MATTER : GASES AND LIQUIDS
DINESH PUBLICATION|Exercise Exercise Fully Solved|23 VideosSTATES OF MATTER (SOLID STATE CHEMISTRY)
DINESH PUBLICATION|Exercise ULTIMATE PREPARATORY PACKAGE|21 VideosSTRUCTURE OF ATOM
DINESH PUBLICATION|Exercise Reason Type Questions|1 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DINESH PUBLICATION-STATES OF MATTER : GASES AND LIQUIDS-Short Answer Type Questions
- Pressure versus volume graph for real gas and are shown in figure. Ans...
Text Solution
|
- Isotherms of carbon dioxide at various temperature are represented in ...
Text Solution
|
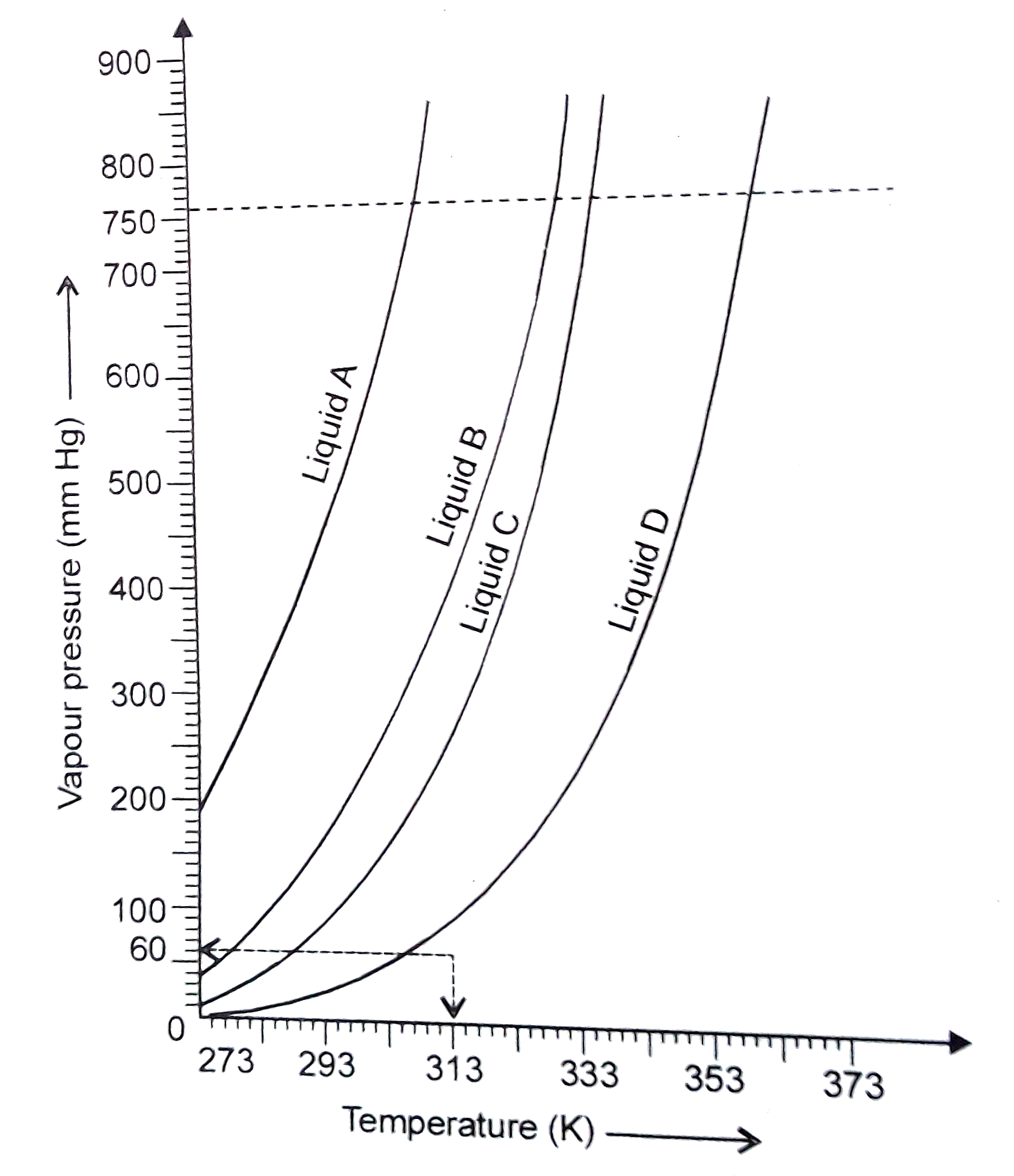
- The variation of vapour pressure of different liquids with temperatu...
Text Solution
|
- Why does the boundary between liquid phase and gaseous phase disappear...
Text Solution
|
- Why does sharp glass edge become smooth on heating it upto its melting...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the term 'laminar flow'. Is the velocity of molecules same in ...
Text Solution
|
- Define gaseous state of a substance.
Text Solution
|
- What is the cause of gas pressure ? How is it measured ?
Text Solution
|
- The pressure of a gas is 2.5 atm. Calculate the value in torr.
Text Solution
|
- What is the difference between barometer and manometer?
Text Solution
|
- BOYLE'S LAW
Text Solution
|
- In what respect does Gay Lussac's law differ form the Charles's law ...
Text Solution
|
- What is the equation of state of an ideal gas ? Why is it so called ?
Text Solution
|
- Show what universal gas constant represents work done per degree per ...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the value of R in : (i) SI units , (II) Cal "degree"^(-1)...
Text Solution
|
- DALTON'S LAW OF PARTIAL PRESSURE
Text Solution
|
- State the law which relates the rate of diffusion of gases to their d...
Text Solution
|
- Derive a relation between density and molar mass of the gas.
Text Solution
|
- How will you justify that the collision among the gas molecules are pe...
Text Solution
|
- Define most probable speed, average speed and root mean square speed ...
Text Solution
|