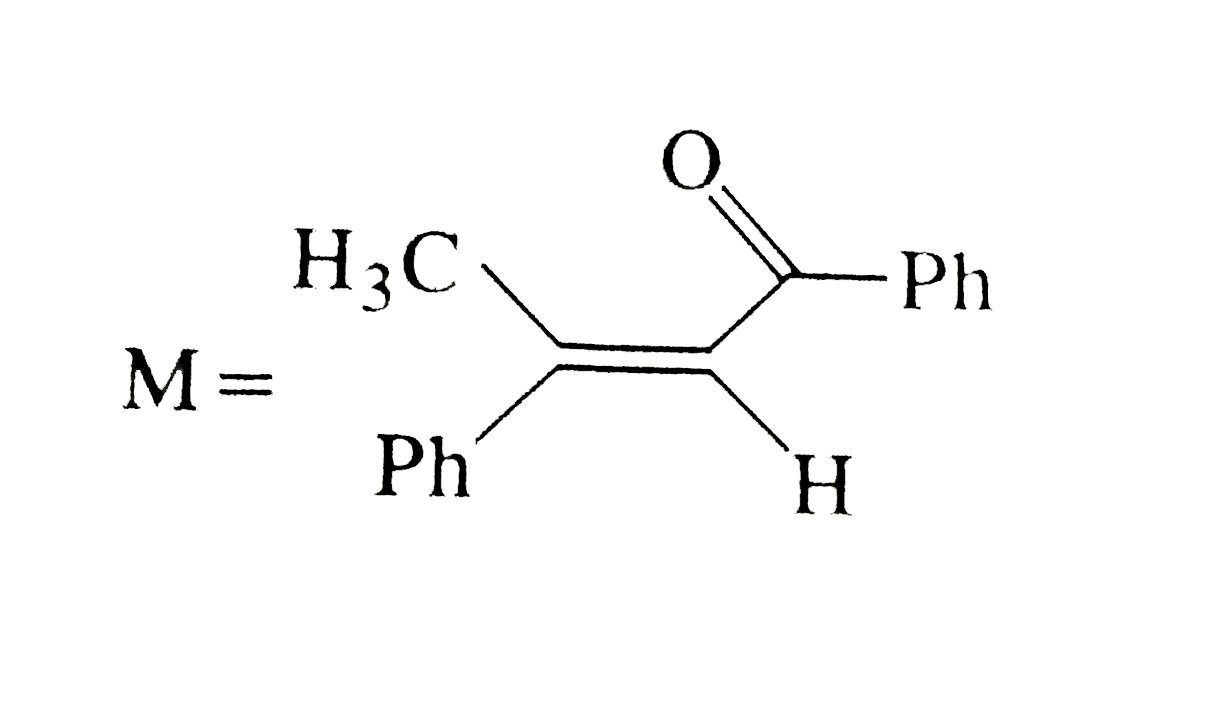
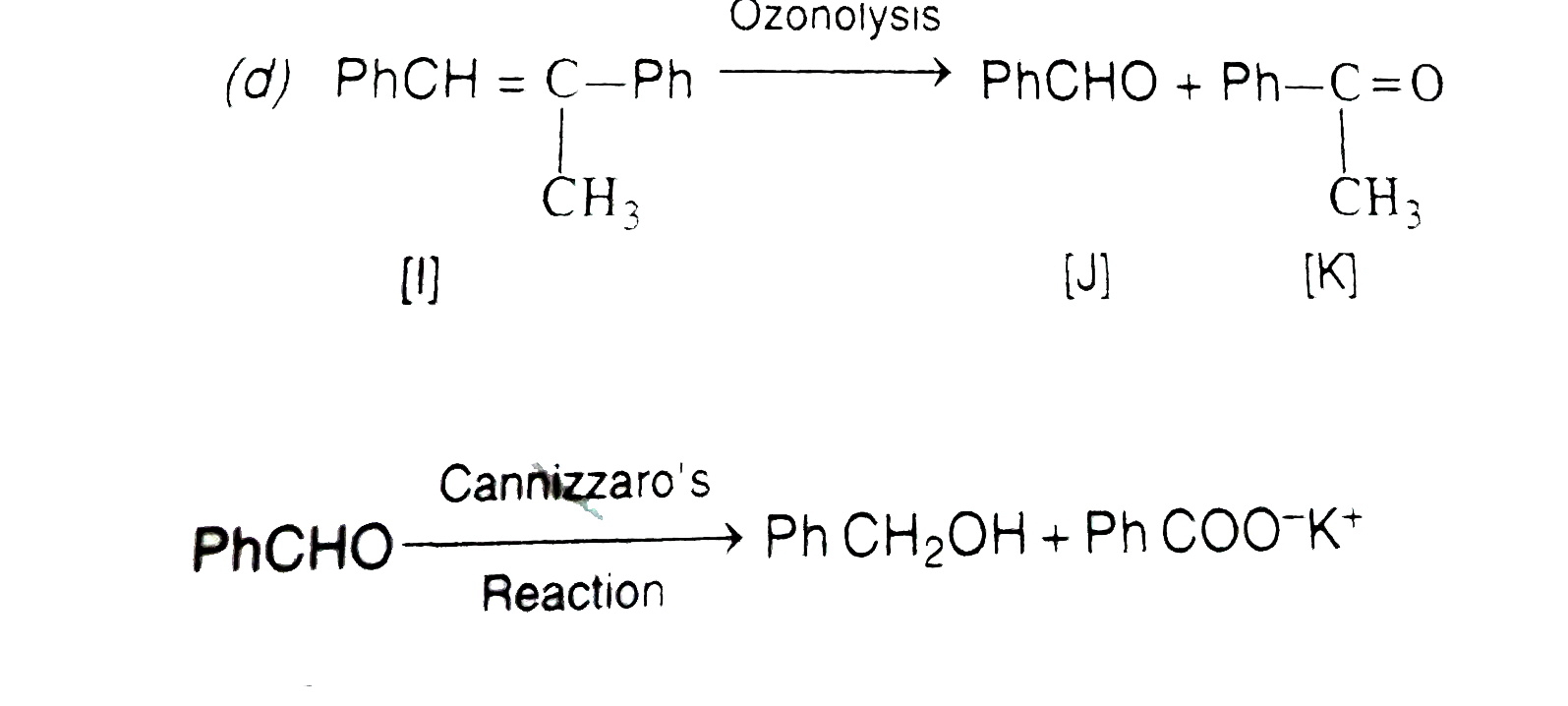A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ALDEHYDES AND KETONES
DINESH PUBLICATION|Exercise Comprehension 6|2 VideosALDEHYDES AND KETONES
DINESH PUBLICATION|Exercise Comprehension 7|2 VideosALDEHYDES AND KETONES
DINESH PUBLICATION|Exercise Comprehension 4|3 VideosALCOHOLS AND PHENOLS
DINESH PUBLICATION|Exercise Matrix|9 VideosALKALI EARTH METALS
DINESH PUBLICATION|Exercise Unit test-12|5 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DINESH PUBLICATION-ALDEHYDES AND KETONES -Comprehension 5
- A tertiary alcohol [H] upon acid catalysed dehydration gives a product...
Text Solution
|
- An acylic hydrocarbon P, having molecular formula C(6)H(10), gives ace...
Text Solution
|
- In the following reaction sequence, the compound J is an intermediate....
Text Solution
|
- In the following reaction sequence, the compound J is an intermediate....
Text Solution
|