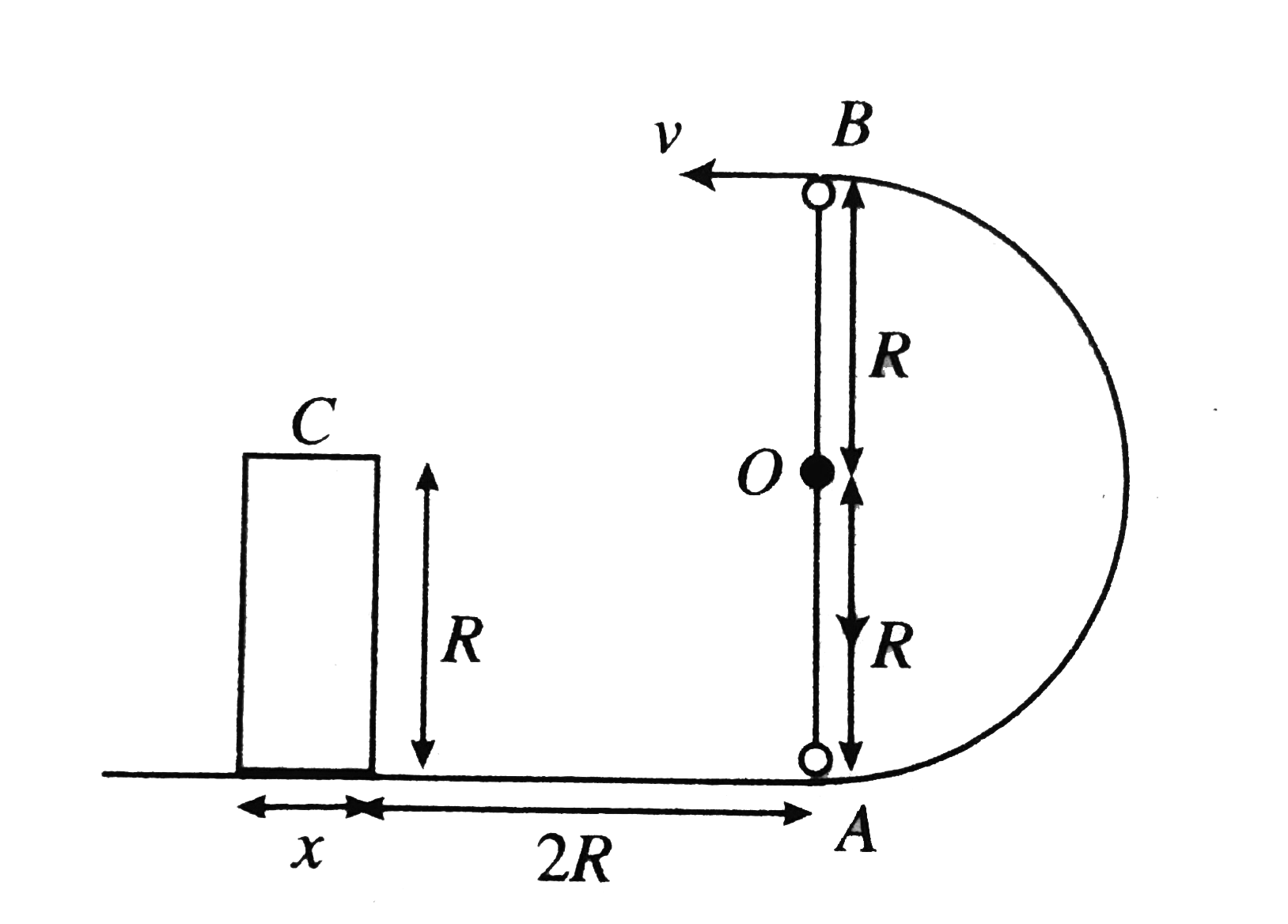
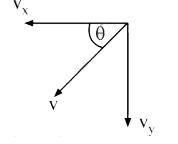
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A small ball is given some velocity at point A towards right so that i...
Text Solution
|
- A small ball is given some velocity at point A towards right so that i...
Text Solution
|
- A small ball is given some velocity at point A towards right so that i...
Text Solution
|
- A small ball is given some velocity at point A towards right so that i...
Text Solution
|
- A ball is released from point A as shown in figure. The ball leaves th...
Text Solution
|
- A ball is released from point A as shown in figure. The ball leaves th...
Text Solution
|
- A player throws a ball vertically upwards with velocity u. At highest ...
Text Solution
|
- A ball is thrown vertically upward. What is the magnitude of velocity ...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows a body A at the top of a frictionless hemispherical inver...
Text Solution
|