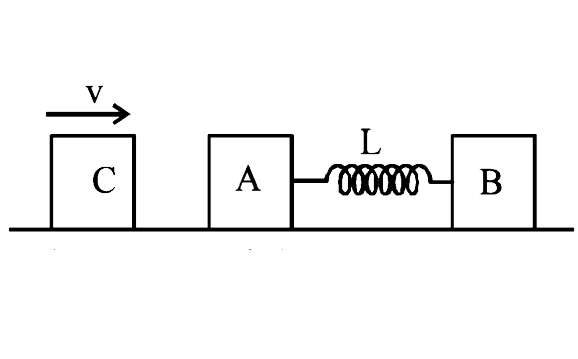
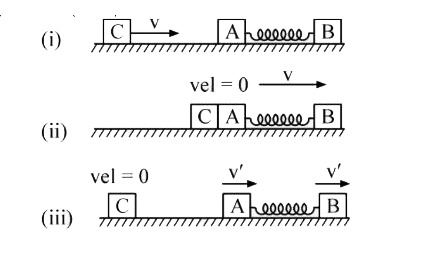
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Recommended Questions
- Two blocks A and B, each of mass m, are connected by a masslesss sprin...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks A and B, each of mass m, are connected by a masslesss sprin...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks A and H . each of mass m , are connected by a massless spri...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks A and B of masses m and 2m are connected by a massless spri...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical blocks A and B , each of mass m resting on smooth floor ...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks A and B each of mass m are connected by a massless spring o...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks A and B each of mass m are connected by a light spring of n...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical blocks A and B, each of mass m resting on smooth floor, ...
Text Solution
|
- m द्रव्यमान के दो ब्लॉक A तथा B एक स्प्रिंग द्वारा जुड़े हैं। स्प्रिंग...
Text Solution
|