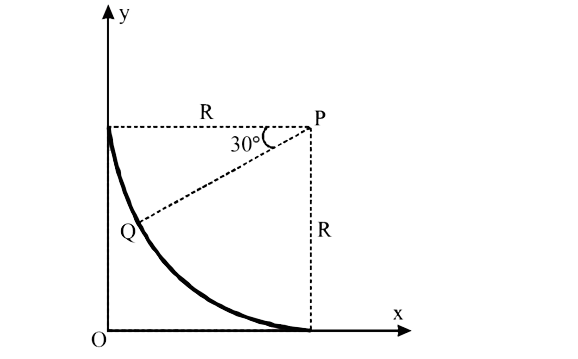
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A small block of mass 1 kg is a circular are of ratius 40 m . The blo...
Text Solution
|
- A small block of mass 1 kg is a circular are of ratius 40 m . The bloc...
Text Solution
|
- A small block of mass 1 kg is a circular are of ratius 40 m . The bloc...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass 5 kg is pulled along a horizontal. The friction coeffi...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass 1 kg is placed at the point A of a rough track shown i...
Text Solution
|
- If the mass of block is 1 kg and a force of 10 / sqrt3 N is applied ho...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass 10 kg is moving on a rough surface as shown in figure....
Text Solution
|
- A small block of mass m slides along a smooth frictional track as show...
Text Solution
|
- एक रुक्ष पृथ के उच्चतम बिन्दु से 1 किग्रा द्रव्यमान के गुटके को विरामा...
Text Solution
|