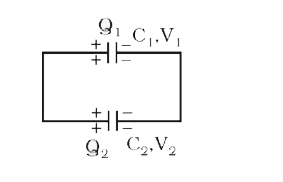
Suppose two charged capacitors `C_(1) and C_(2)` charged to potentials `V_(1) and V_(2)` are connected in parallel, with their positive terminals connected together and negative terminals connected together as shown in the figure. After connection, the charge redistributes in such a way that the potential differences across `C_(1) and C_(2)` become equal charges on capacitors before connection, `Q_(1)=C_(1)V_(1),Q_(2)=C_(2)V_(2)`
Common potential after connection, `V=(Q_(1)+Q_(2))/(C_(1)+C_(2))`
`V=(C_(1)V_(1)+C_(2)V_(2))/(C_(1)+C_(2))` . .. (i)
If `Q_(1)'` and `Q_(2)'` are charges after sharing then `Q_(1)'=C_(1)V,Q_(2)'=C_(2)V`
`implies (Q_(1)')/(Q_(2)')=(C_(1))/(C_(2))` . .. (ii)
This means that after connection, the charges on capacitors are shared in ratio of their capacitances.
Electrostatic energy stored in the system: When charges are shared between two capacitors, then some energy is dissipated as heat and hence, definitely there is a loss of energy
The energy loss=Initial energy `(U_(i))-`Final energy `(U_(f))`: Initial energy `U_(i)=(1)/(2)C_(1)V_(1)^(2)+(1)/(2)C_(2)V_(2)^(2)`
After connection two capacitors, their combined capacitance is `(C_(1)+C_(2))` and common potential is V, therefore, final electrostatic energy `U_(f)=(1)/(2)(C_(1)+V_(2))V^(2)`
`=(1)/(2) (C_(1)+C_(2))((C_(1)V_(1)+C_(2)V_(2))/(C_(1)+C_(2)))^(2)` (using (i)) : `=(1)/(2)((C_(1)V_(1)+C_(2)V_(2))^(2))/((C_(1)+C_(2)))`
`therefore`Loss in energy during sharing of charges `DeltaU=U_(i)-U_(f)`.
`=(1)/(2)C_(1)V_(1)^(2)+(1)/(2)C_(2)V_(2)^(2)-((1)/(2)(C_(1)V_(1)+C_(2)V_(2))^(2))/(C_(1)+C_(2))=((C_(1)+C_(2))(C_(1)V_(1)^(2)+C_(2)V_(2)^(2))-(C_(1)V_(1)+C_(2)V_(2))^(2))/(2(C_(1)+C_(2)))`
`=(1)/(2(C_(1)+C_(2))){C_(1)^(2)V_(1)^(2)+C_(1)C_(2)V_(2)^(2)+C_(1)C_(2)V_(1)^(2)+C_(2)^(2)V_(2)^(2)-(C_(1)^(2)V_(1)^(2)+C_(2)^(2)V_(2)^(2)+2C_(1)C_(2)V_(1)V_(2))}`
`=(1)/(2(C_(1)+C_(2))){C_(1)C_(2)V_(2)^(2)-C_(1)C_(2)V_(1)^(2)-2C_(1)C_(2)V_(1)V_(2)}`
`=(C_(1)C_(2))/(2(C_(1)+C_(2))){V_(1)^(2)+V_(2)^(2)-2V_(1)V_(2)}=(C_(1)C_(2))/(2(C_(1)+C_(2)))(V_(1)-V_(2))^(2)`
i.e., Energy loss, `DeltaU=(C_(1)C_(2))/(2(C_(1)+C_(2)))(V_(1)-V_(2))^(2)`.
As `C_(1)C_(2) and (V_(1)-V_(2))^(2)` are all positive, therefore, `DeltaU` is always positive. thus, in the process of redistribution of charges, there is always a loss of energy. this energy is lost in the lost in the form of heat in connecting wire.