Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
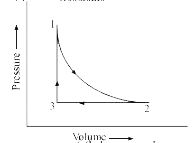
- (a) A sample of 1.0 mol of a monoatomic ideal gas is taken through a ...
Text Solution
|
- The temperature dependence of equilibrium constant of a reaction is gi...
Text Solution
|
- For the reaction at 300K A(g) hArr V(g)+S(g) Delta(r) H^(@)=-30kJ //mo...
Text Solution
|
- For the reation at 300 K A(g)hArrV(g)+S(g) Delta(r)H^(@)=-kJ//mol,...
Text Solution
|
- (a) A sample of 1.0 mol of a monoatomic ideal gas is taken through a ...
Text Solution
|
- Which quantity out of Delta(r)G " and " Delta(r) G^(Θ) will be zero at...
Text Solution
|
- Which quantity out of Delta(r)G and Delta(r)G^(c-) will be zero at equ...
Text Solution
|
- साम्यावस्था पर Delta(r)G तथा Delta(r)G^(@) में से कौन-सी राशि का मान श...
Text Solution
|
- (a) A sample of 1.0 mol of a monoatomic ideal gas is taken through a ...
Text Solution
|