A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
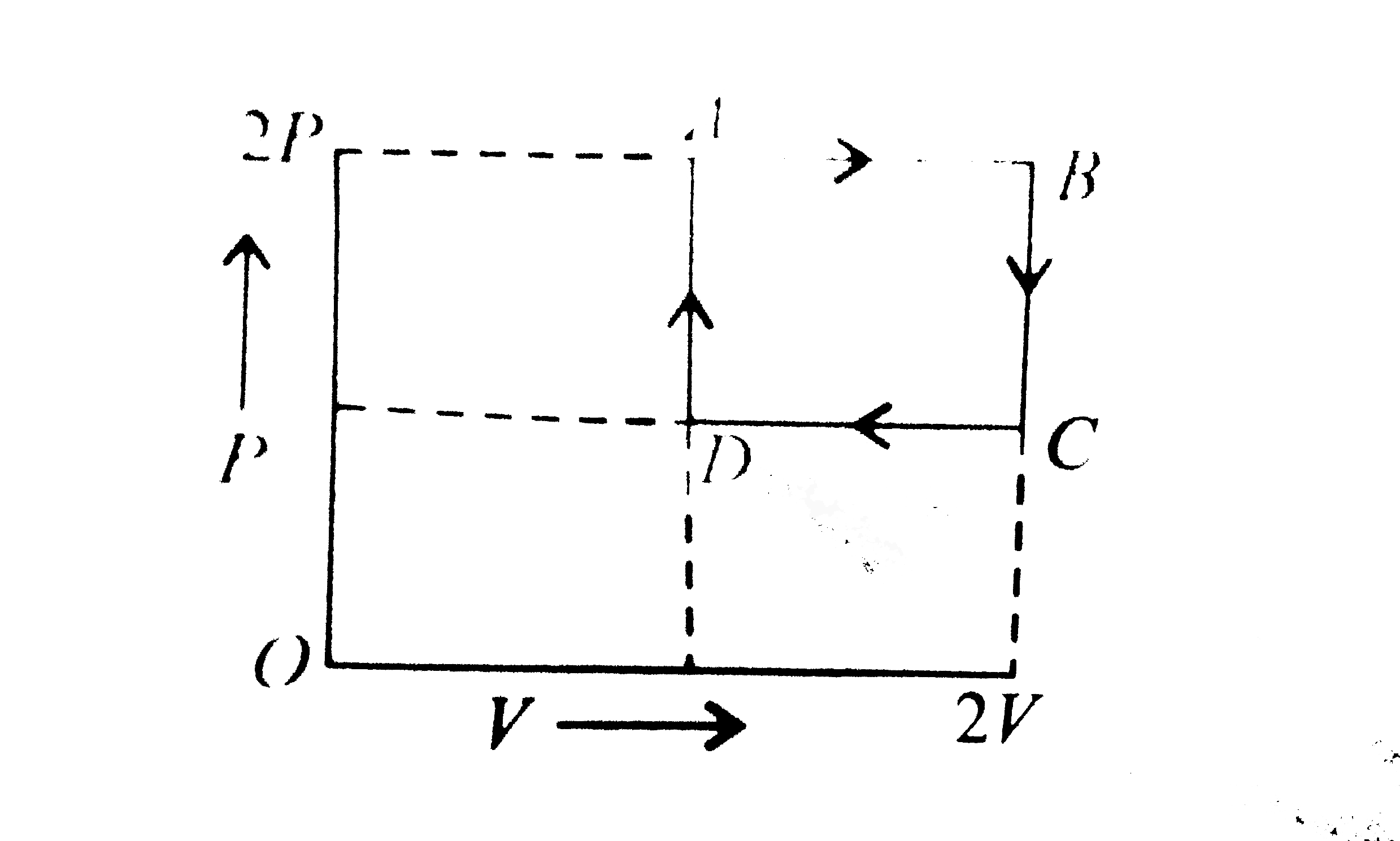
- The state of a mole of an ideal gas changed from state A at pressure 2...
Text Solution
|
- The state of a mole of an ideal gas changed from state A at pressure 2...
Text Solution
|
- The state of a mole of an ideal gas changed from state A at pressure 2...
Text Solution
|
- The state of a mole of an ideal gas changed from state A at pressure 2...
Text Solution
|
- The state of a mole of an ideal gas changed from state A at pressure 2...
Text Solution
|
- The state of a mole of an ideal gas changed from state A at pressure 2...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of an ideal gas going from state-A to state-B through differe...
Text Solution
|
- The state of a mole of an ideal gas changed from state A at pressure 2...
Text Solution
|
- The state of a mole of an ideal gas changed from state A at pressure 2...
Text Solution
|