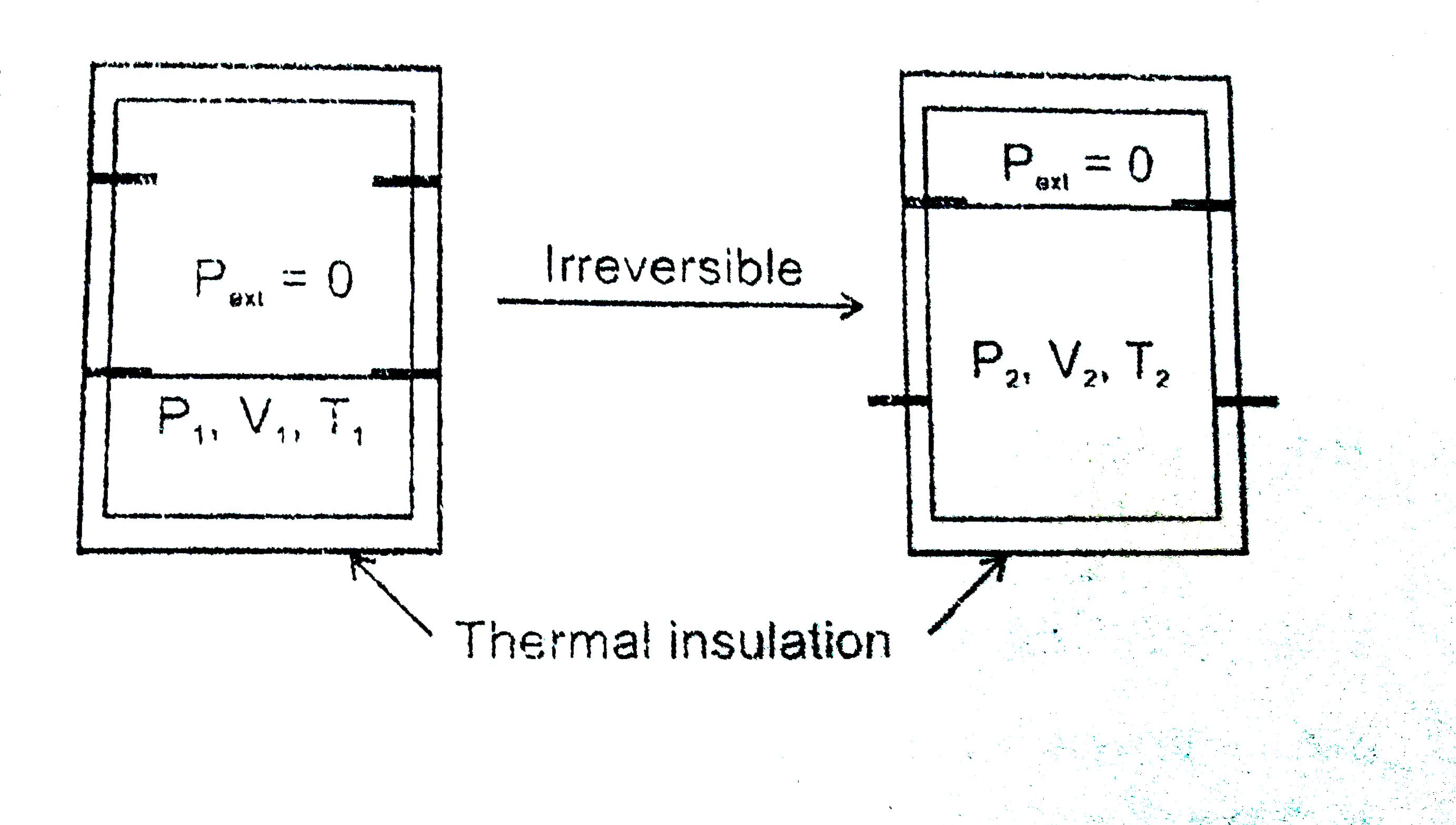A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- An ideal gas in a thermally insulated vessel at internal pressure =P(1...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal gas expands isothermally from volume V(1) to V(2) and is then...
Text Solution
|
- Two thermally insulated vessels are filled with an ideal gas. The pres...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal gas in thermally insulated vessel at internal (pressure)=P(1)...
Text Solution
|
- Two gases which are at pressure p(1) volume V(1) and temperature T(1) ...
Text Solution
|
- Two thermally insulated vessels 1 and 2 are filled with air and connec...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal gas in a thermally insulated vessel at internal pressure =P(1...
Text Solution
|
- Two thermally insulated vessel 1 and 2 are filled with air at temperat...
Text Solution
|
- The initial pressure, temperature & volume of 1 mol of a gas are P(1),...
Text Solution
|