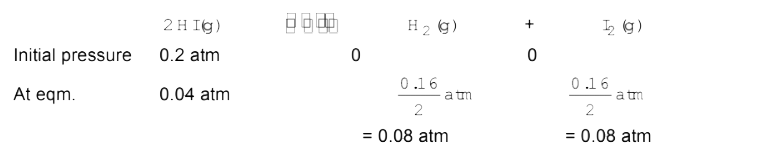Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A sample of HI(g) is placed in flask at a pressure of 0.2 atm. At equi...
Text Solution
|
- A sample of HI(g) is placed in flask at a pressure of 0.2 atm. At equi...
Text Solution
|
- K(p)=0.04 atm at 899 K for the equilibrium shown below. What is the eq...
Text Solution
|
- A sample of HI(g) is placed in flask at a pressure of 0.2 atm. At equi...
Text Solution
|
- HI(g) का एक नमूना 0.2 atm दाब पर एक फ्लक्स में रखा जाता है। साम्य पर H...
Text Solution
|
- A sample of HI(g) is placed in flask at a pressure of 0.2 atm. At equi...
Text Solution
|
- K(p)=0.04 atm at 899 K for the equilibrium shown below. What is the eq...
Text Solution
|
- A sample of HI(g) is placed in flask at a pressure of 0.2atm. At equil...
Text Solution
|
- A sample of HI (g) is placed in a flask at a pressure of 0.2atm. In ca...
Text Solution
|