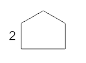
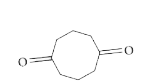
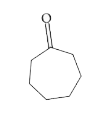
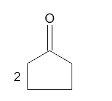
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Reductive Ozonolysis of will give
Text Solution
|
- BY REDUCTIVE OZONOLYSIS:
Text Solution
|
- On reductive ozonolysis, ethylene gives
Text Solution
|
- 1-Butyne on reductive ozonolysis gives.
Text Solution
|
- Reductive ozonolysis of o-sylene gives
Text Solution
|
- Which of the folllowing on reductive ozonolysis will give only glyoxal...
Text Solution
|
- Give the product(s) of reductive ozonolysis of the following compounds...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following on reductive ozonolysis give only glyoxal?
Text Solution
|
- An alkene on reductive ozonolysis gives two molecules of CH(2)(CHO)(2...
Text Solution
|
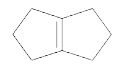 will give
will give