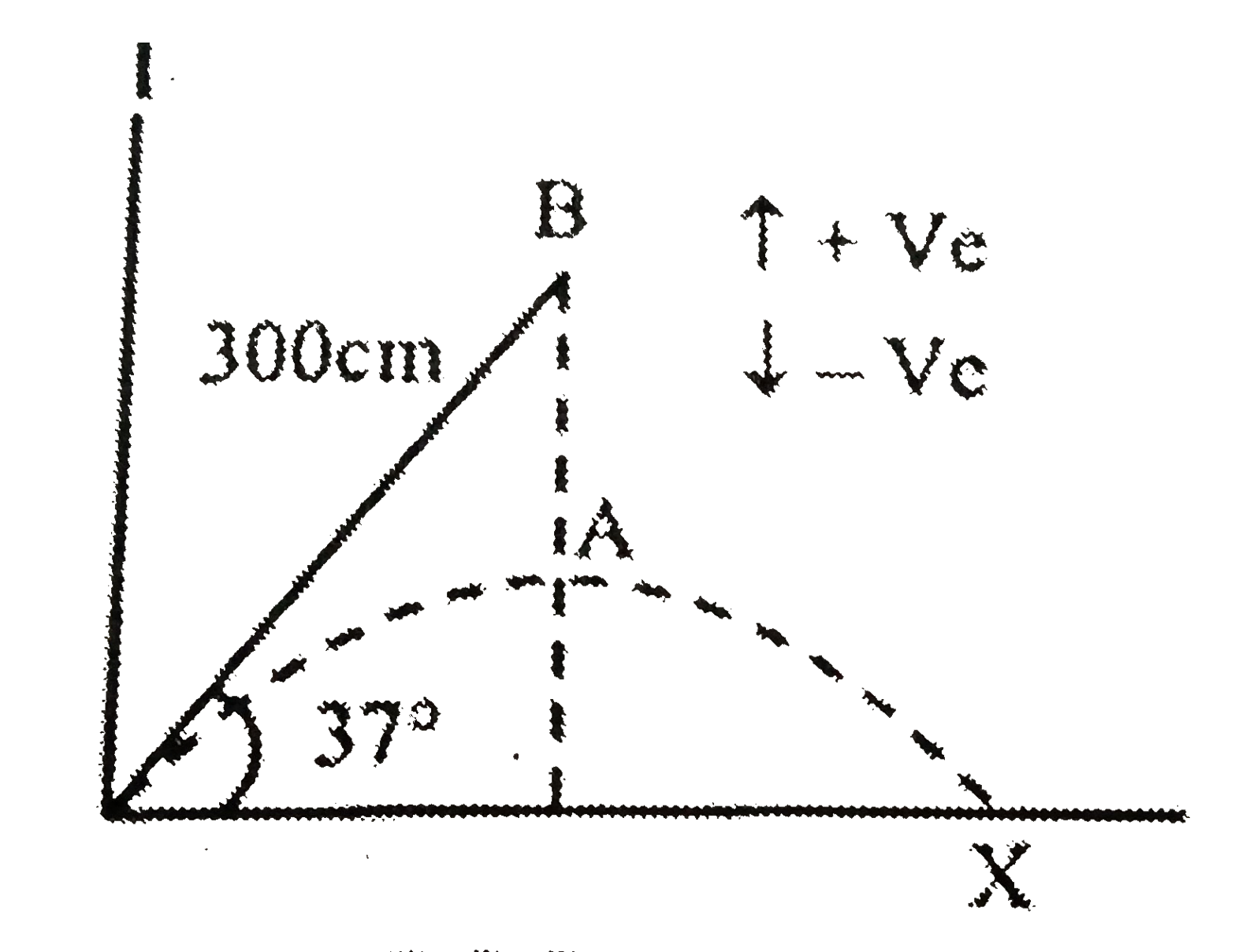A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CAREER POINT-MOCK TEST 4-CHEMISTRY
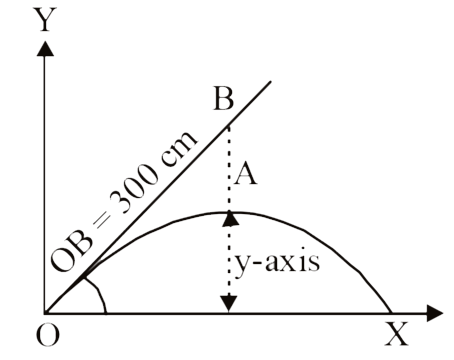
- A ball 'A' is projected from origin with an initial velocity v(0) = 70...
Text Solution
|
- Which is in the decreasing order of boiling points of V group hydrid...
Text Solution
|
- The process used for the removal of hardness of water is
Text Solution
|
- The product of the reaction is -
Text Solution
|
- Which one of the following compounds undergoes predominantly SN^2 reac...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the compounds HCHO (I),CH(3)CH(2)CHO (II), CH(3)COCH(3) (III)...
Text Solution
|
- The oxidation state of S-atoms in Caro's and Marshall's acids are:
Text Solution
|
- 25mL of 2N HCl, 50 mL "of" 4N HNO(3) and xmL H(2)SO(4) are mixed toget...
Text Solution
|
- An aqueous solution containing 1M each of Au^(3+),Cu^(2+),Ag^(+),Li^(...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following statement is not correct?
Text Solution
|
- In which transformation the change of hydridization and shape about un...
Text Solution
|
- The correct order of second ionization energy of C,N,O and F are in th...
Text Solution
|
- The ionization energy of the electron in the lowest orbit of hydrogen ...
Text Solution
|
- A binary solid(A^(+) B^(-)) has a zinc blende stracture with B ions co...
Text Solution
|
- Given: (i) Cu^(2+)+2e^(-) rarr Cu, E^(@) = 0.337 V (ii) Cu^(2+)+e^...
Text Solution
|
- When heated , ammonium carbamate decomate decompoes as follows : NH(...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate elevation in boiling point for 2 molal aqueous solution of g...
Text Solution
|
- Given that for a reaction of order n. the intergrated form of the rate...
Text Solution
|
- Solubility of calcium phosphate (molecular mass, M) in water is W g pe...
Text Solution
|
- When 1 L of CO2 is heated with graphite , the volume of the gases coll...
Text Solution
|
- Periodic acid splits glucose and fructose into formaldehyde and formic...
Text Solution
|