Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT EXEMPLAR-COORDINATION COMPOUNDS-Coordination Compounds
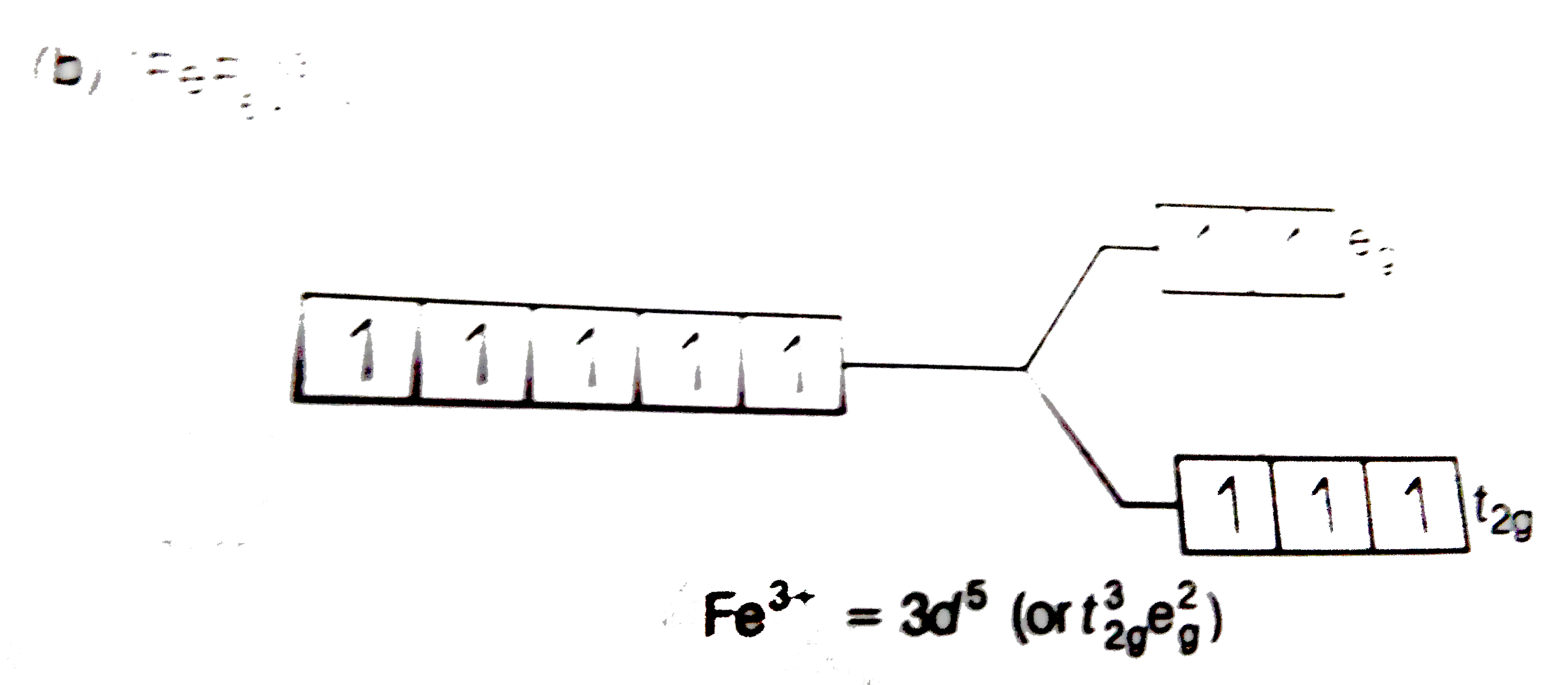
- Explain why [Fe(H(2)O)(6)]^(3+) has magnetic moment value of 5.92 BM w...
Text Solution
|
- Arrange following complex ions in increasing order of crystal field sp...
Text Solution
|
- Why do compounds having similar geometry have different magnetic momen...
Text Solution
|
- CuSO(4).5H(2)O is blue in colour while CuSO(4) is colourless. Why ?
Text Solution
|
- Name the type of isomerism when ambidentate ligands are attched to cen...
Text Solution
|
- Match the complex ions given in column I with the colours given in col...
Text Solution
|
- Match the coordination compounds given in column I with the central me...
Text Solution
|
- Match the complex ions given in column I with the hybridisation and nu...
Text Solution
|
- Match the complex species given in column I with the possible isomeris...
Text Solution
|
- Match the compounds given In column I with oxidation state of cabalt p...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion (A) Toxic metal ions are removed by the chelating ligands. ...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion (A) [Cr(H(2)O(6))]Cl(2) and [Fe(H(2)O)(6)]Cl(2) are reducing...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion (A) Linkage isomerism arises in coordination compounds conta...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion (A) Complexes of MX(6) and MX(5)L type (X and L are unidenta...
Text Solution
|
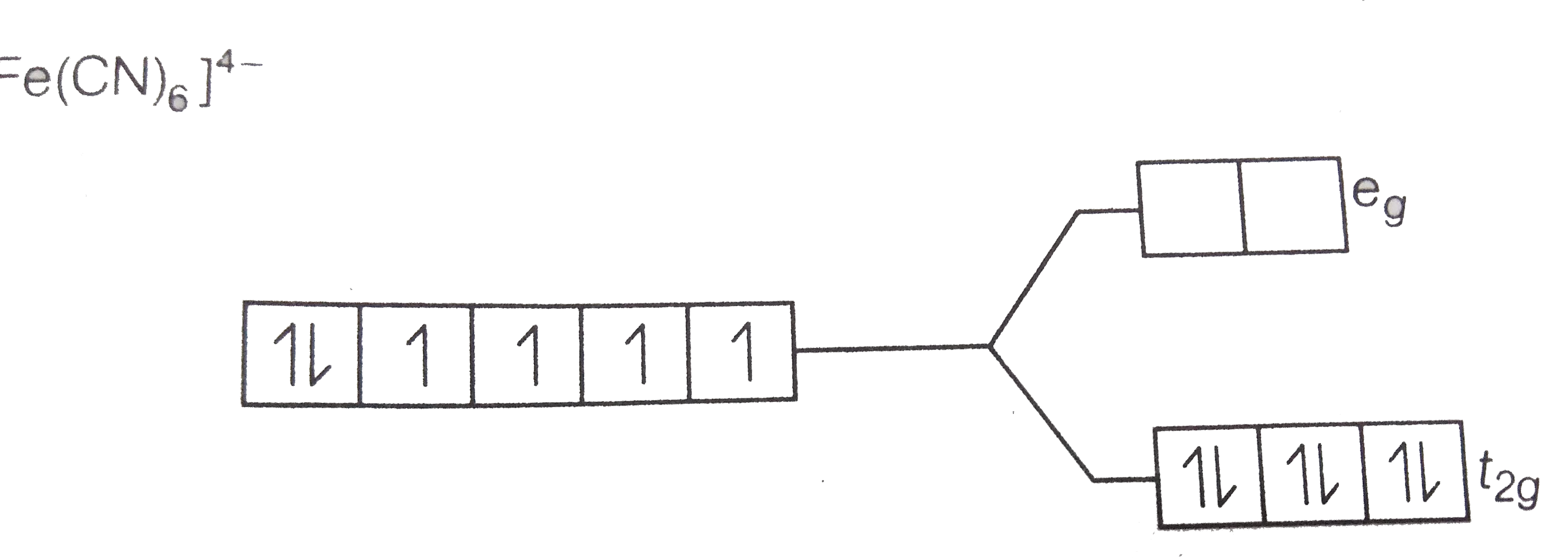
- Assertion (A) [Fe(CN)(6)]^(3-) ion shows magnetic moment corresponding...
Text Solution
|
- Using crystal field theory, draw energy level diagram, write electroni...
Text Solution
|
- Using valence bond theory, explain the following in relation to the co...
Text Solution
|
- CoSO(4)Cl.5 NH(3) exists in two isomeric forms 'A' and 'B'. Isomer 'A'...
Text Solution
|
- what is the relationsphip between observed colour of the complex and t...
Text Solution
|
- Why are different colours observed in octahedral and tetrahedral compl...
Text Solution
|