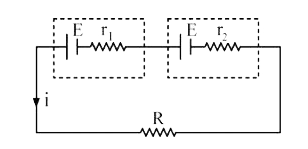A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- In the given circuit, if the potential difference across the internal ...
Text Solution
|
- Two sources of equal emf are connected to an external resistance R. Th...
Text Solution
|
- Two sources of current of equal emf are connected in series and having...
Text Solution
|
- If the external resistance is equal to internal resistance of a cell o...
Text Solution
|
- A battery of emf E and internal resistance r is connected across a res...
Text Solution
|
- If E is the emf of a cell of internal resistance r and external resist...
Text Solution
|
- A cell having an emf E and internal resistance r is connected across a...
Text Solution
|
- In the given circuit, if the potential difference across the internal ...
Text Solution
|
- Two cells of internal resistance r1 and r2 and of same emf are connect...
Text Solution
|