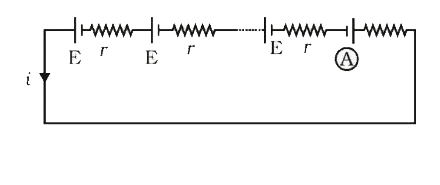
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- n identical cells, each of emf epsilon and internal resistance r, are ...
Text Solution
|
- n identical cells, each of emf E and internal resistance r, are joined...
Text Solution
|
- n identical cells, each of emf epsilon and internal resistance r, are ...
Text Solution
|
- n identical cells, each of emf epsilon and internal resistance r, are ...
Text Solution
|
- n identical calls are joined in series with its two cells A and B in l...
Text Solution
|
- n identical cells are joined in series with two cells A and B with rev...
Text Solution
|
- n identical cells, each of emf epsilon and internal resistance r, are ...
Text Solution
|
- n identical cells each of emfe and internal resistance r are joined in...
Text Solution
|
- n identical cells, each of emf epsilon and iternal resistance r, are j...
Text Solution
|