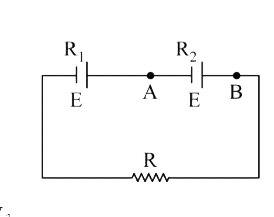
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Two sources of equal emf are connected to an external resistance R. Th...
Text Solution
|
- Two cells, having the same emf, are connected in series through an ext...
Text Solution
|
- Two batteries of E(1) internal resistance r(1) & emf E(2) internal res...
Text Solution
|
- Two sources of equal emf are connected to an external resistance R. Th...
Text Solution
|
- An accumulator of emf epsilon and internal resistance r is first conne...
Text Solution
|
- An accumulator of emf epsilon and internal resistance r is first conne...
Text Solution
|
- Two cells of same emf epsilon , but different internal resistances r(1...
Text Solution
|
- A resistance R(1) is connected to a source of constant voltage . On co...
Text Solution
|
- [" 27.Two cells of same emf "E" but of different internal resistance "...
Text Solution
|