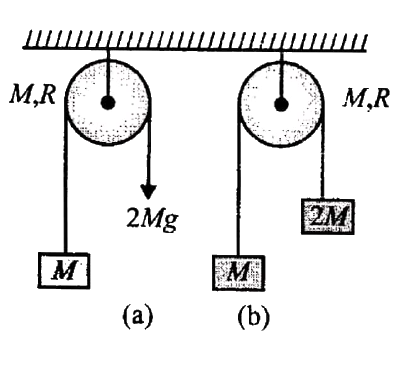
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A cord is wrapped on a pulley (disk) of mass M and radius R as shown i...
Text Solution
|
- A mass m is attached to a pulley through a cord as shown in figure. Th...
Text Solution
|
- Blocks of mass M(1) and M(2) are connected by a cord which passes over...
Text Solution
|
- चित्र में दिखाई गई परिस्थिति में द्रव्यमान M के गुटके का त्वरण ज्ञात क...
Text Solution
|
- द्रव्यमान M तथा त्रिज्या R की एकसमान डिस्क एक क्षैतिज अक्ष पर स्थित है...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m on a smooth horizontal surface is. Connected to a se...
Text Solution
|
- A cord is wrapped on a pulley (disk) of mass M and radius R as shown i...
Text Solution
|
- A light thread is wound on a disk of mass m and other end of thread is...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure shown, all surfaces are smooth and the pulley is massles...
Text Solution
|