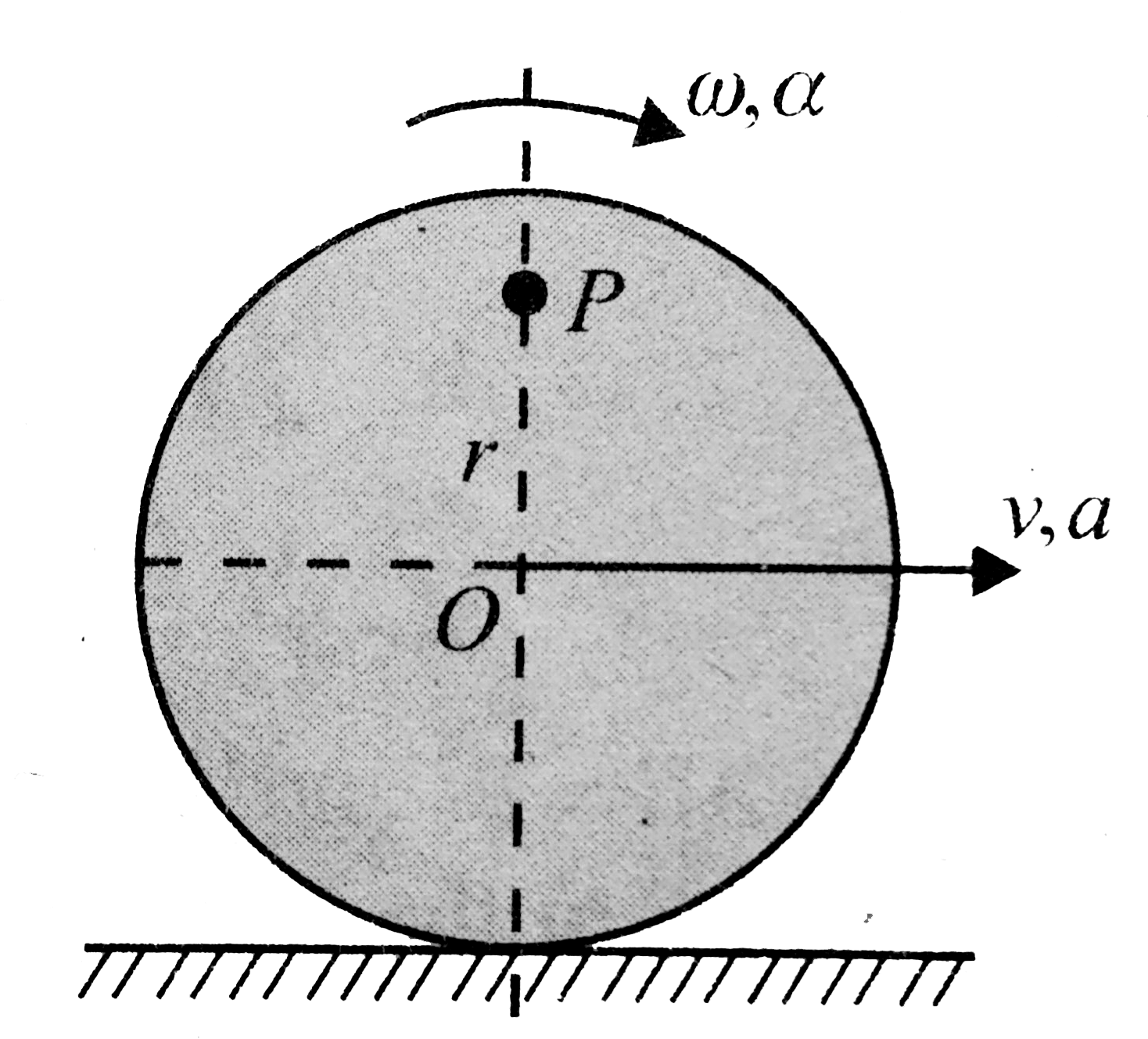
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A disc of radius R rolls on a horizontal ground with linear accelerati...
Text Solution
|
- Two point P and Q. diametrically opposite on a disc of radius R have l...
Text Solution
|
- A ring of radius R rolls on a horizontal surface with constant acceler...
Text Solution
|
- A uniiform disc of radius r spins with angular velocity omega and angu...
Text Solution
|
- A disc of radius R rolls on a horizontal ground with linear accelerati...
Text Solution
|
- A wheel is rolling on a horizontal plane. At a certain instant it has ...
Text Solution
|
- A disc with linear velocity v and angular velocity omega is placed on ...
Text Solution
|
- A sphere of radius r is rolling without slipping on a hemispherical su...
Text Solution
|
- In nonuniform circular motion, the linear acceleration vec a , the ang...
Text Solution
|