A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
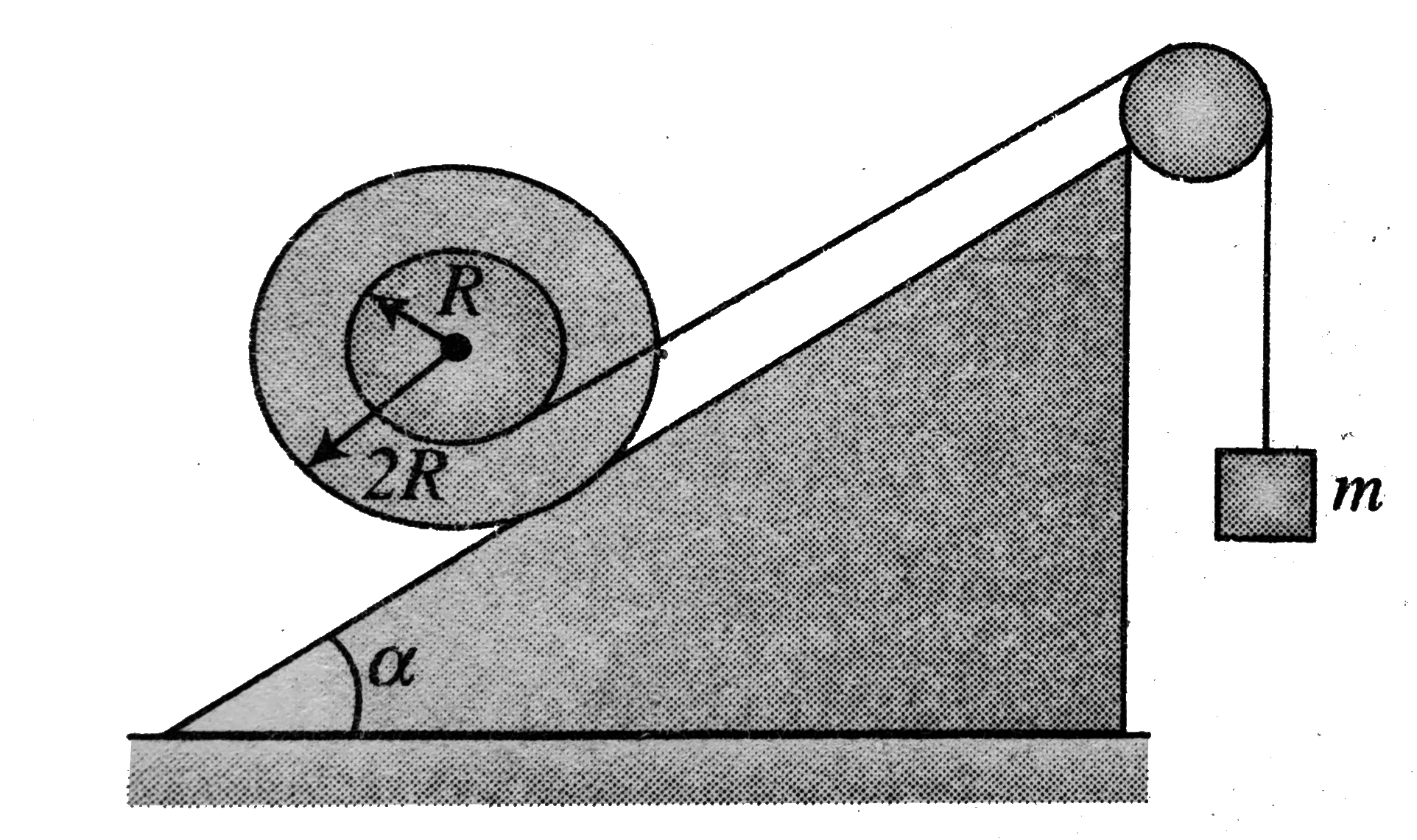
- A spool of mass M and radius 2R lies on an inclined plane as shown in ...
Text Solution
|
- A spool (consider it as a double disc system joined by a short tube at...
Text Solution
|
- A spool of mass M and radius 2R lies on an inclined plane as shown in ...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows a spool with thread wound on it placed on a smooth plane ...
Text Solution
|
- A spool with a thread wound on it is placed on an inclined smooth plan...
Text Solution
|
- Consider an arrangement shown in the figure. The pulley P is frictionl...
Text Solution
|
- A spool with a thread wound on it is placed on a smooth inclined plane...
Text Solution
|
- A spool is kept in equilibrium on an incline plane as shown in figure....
Text Solution
|
- A spool has the shape shown in figure. Radii of inner and outer cylind...
Text Solution
|