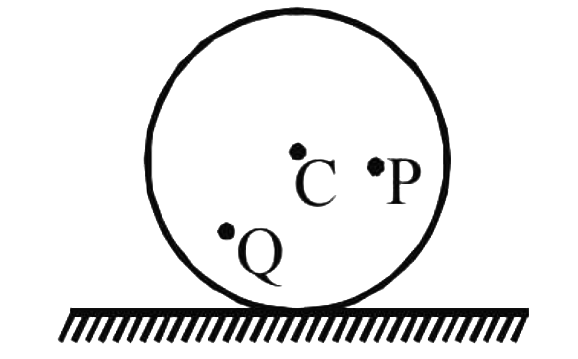
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A disc is rolling without slipping with angular velocity omega. P and ...
Text Solution
|
- A disc is rolling without slipping with angular velocity omega . P and...
Text Solution
|
- the disc of the radius r is confined to roll without slipping at A an...
Text Solution
|
- A disc is rolling on an inclined plane without slipping. The velocity ...
Text Solution
|
- A disc is rolling (without slipping) on a horizontal surface. C is its...
Text Solution
|
- As shown in the figure, a disc of mass m is rolling without slipping w...
Text Solution
|
- A disc of the radius R is confined to roll without slipping at A and B...
Text Solution
|
- A disc is rolling without slipping on a horizontal surface with C, as ...
Text Solution
|
- एक वृत्ताकार डिस्क एक क्षैतिज तल पर बिना फिसले एकसमान कोणीय चाल omega ...
Text Solution
|