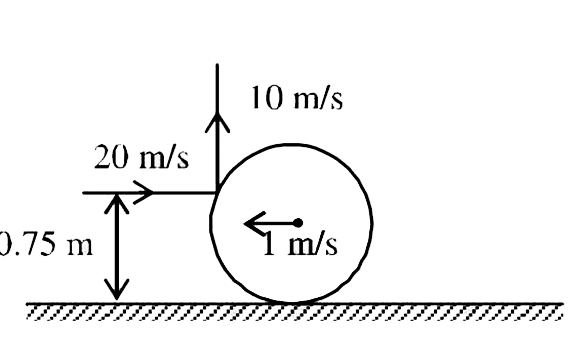A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A thin ring of mass 2kg and radius 0.5 m is rolling without on a horiz...
Text Solution
|
- A thin ring of mass 2kg and radius 0.5 m is rolling without slipping o...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of mass M moving with a velocity v collides perfectly inelastic...
Text Solution
|
- As shown in the figure a body of mass m moving horizontally with spee...
Text Solution
|
- A ring of mass 1kg and radius 1m is moving with a velocity of 1m//s by...
Text Solution
|
- X- अक्ष में, 0.1 किग्रा द्रव्यमान की एक गेंद 4.0 मीटर/सेकण्ड के वेग स...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform thin ring of mass 0.4kg rolls without slipping on a horizont...
Text Solution
|
- Two balls of equal masses movin with velocities 10m/s and -7m/s respec...
Text Solution
|
- 2kg द्रव्यमान तथा 0.2m व्यास का एक खोखला गोला एक नत समत पर 0.5 m/s के...
Text Solution
|