Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Recommended Questions
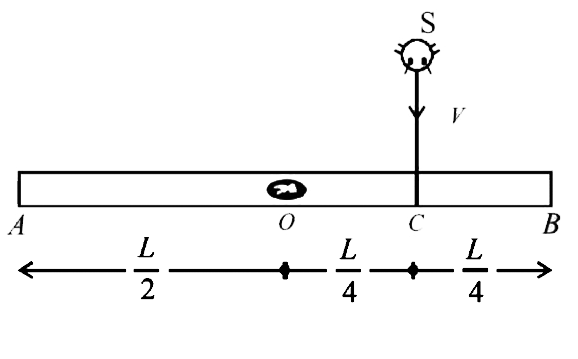
- A thin uniform bar lies on a frictionless horizonta surface and is fre...
Text Solution
|
- A thin uniform bar lies on a frictionless horizonta surface and is fre...
Text Solution
|
- Two bodies of masses 1 kg and 2 kg are moving in two perpendicular dir...
Text Solution
|
- Two particles of mass 1 kg and 0.5 kg are moving in the same direction...
Text Solution
|
- A body of mass 2 kg is moving with velocity 10 m / s towards east. Ano...
Text Solution
|
- A thin uniform bar lies on a frictionless horizontal surface and is fr...
Text Solution
|
- 25 kg द्रव्यमान का एक बालक 10kg द्रव्यमान के तख्ते पर खड़ा है। यह तख्त...
Text Solution
|
- In the arrangement as shown, block A of mass 3 kg moves towards left w...
Text Solution
|
- 10 किग्रा द्रव्यमान का पिण्ड एक घर्षण रहित क्षैतिज पृष्ठ पर 5 मी/से के...
Text Solution
|