A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT EXEMPLAR-THERMODYNAMICS-Multiple choice questions
- delta(f) U^(Ó¨) "of formation of" CH(4)(g) at a certain temperature is...
Text Solution
|
- In an adibatic process, no transfer of heat takes place between system...
Text Solution
|
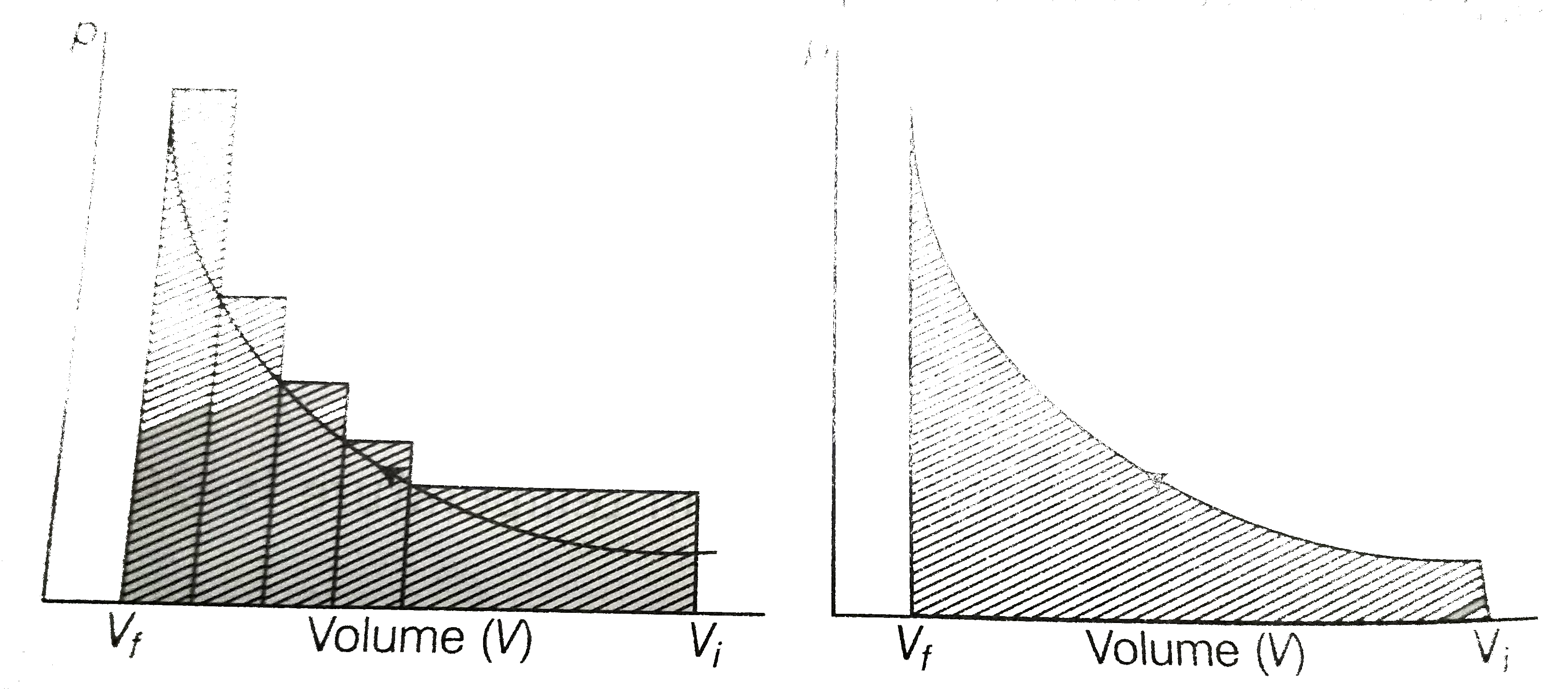
- The pressure volume work for an ideal gas can be calculated by using t...
Text Solution
|
- The entropy change can be calculated by using the expression DeltaS-(q...
Text Solution
|
- On the basic of thermochemical equations (I),(II)and (III), Find out w...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the reactions given below .On the basis of these reactions ,F...
Text Solution
|
- The enthalpy of elements in their standard atates are taken as zero .T...
Text Solution
|
- Enthalpy of sublimation of a substance is equal to :
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following is not correct ?
Text Solution
|
- Thermodynamics mainly deals with:
Text Solution
|
- In an exothermic reaction heat is evolved and system loses heat to the...
Text Solution
|
- The spontaneity means having the potential to proceed without assistan...
Text Solution
|
- For an ideal gas, the work of reversible expansion under isothermal co...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the following reaction between zinc and oxygen and choose t...
Text Solution
|
- 18.0 g of water completely vaporises at 100^(@)C and 1 bar pressure an...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of acetone requires less heat to vaporise than 1 mole of wate...
Text Solution
|
- Standard molar enthalpy of formation, Delta(f) H^(Θ) is just a special...
Text Solution
|
- The value of Delta(f) H^(Θ) for NH(3) is -91.8 kJ mol^(-1). Calculate ...
Text Solution
|
- Enthalpy is an extensive property. In general, if enthalpy of an overa...
Text Solution
|
- The enthaply of atomisation for the reaction : CH(4)(g) to C(g) + 4 H(...
Text Solution
|