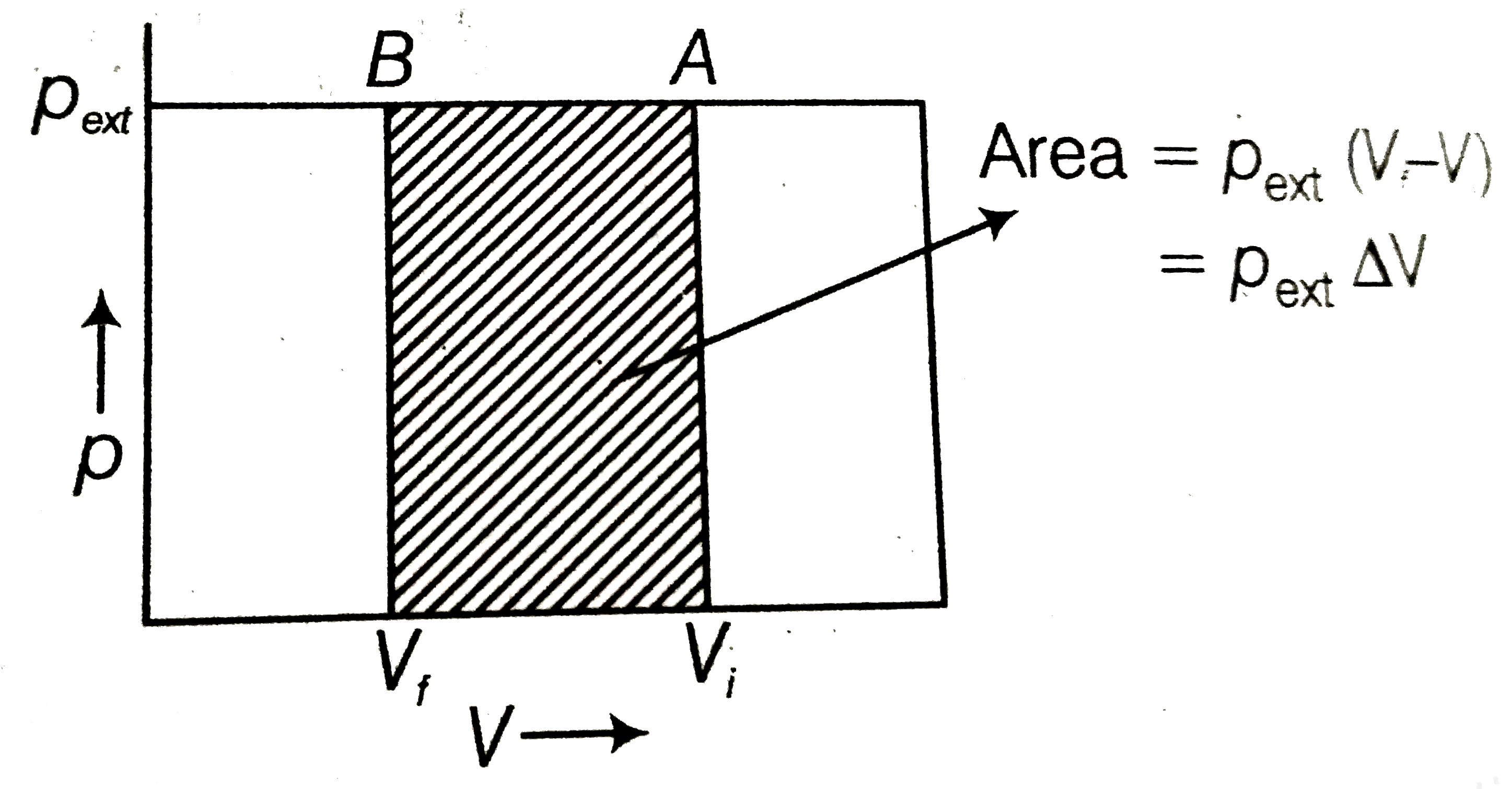
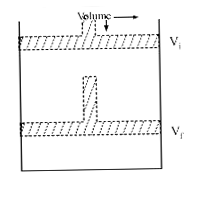Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT EXEMPLAR-THERMODYNAMICS-Multiple choice questions
- The enthalpy of vaporisation of C CI(4) is 30.5 kJ "mol"^(-1).Calcul...
Text Solution
|
- The enthalpy of reaction for thr equation 2H2(g) +O2(g) rarr 2H2O(l)...
Text Solution
|
- What will be the work done on an ideal gas enclosed in a cylinder, whe...
Text Solution
|
- How will you calculate work done on an ideal gas in a compression, whe...
Text Solution
|
- Represent the potential energy/enthalpy change in the following proces...
Text Solution
|
- Enthalpy diagram for a particular reaction is given in figure. Is it p...
Text Solution
|
- 1.0 mol of a monoatomic ideal gas is expanded from state (1) to state ...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal gas is allowed to expand against a constant pressure of 2 bar...
Text Solution
|
- Match the following
Text Solution
|
- Match the following processes with entropy change
Text Solution
|
- Match the following parameters with description for spontaneity
Text Solution
|
- Match the following
Text Solution
|
- Assertion (A). Combustion of all organic compounds is an exothermic re...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion (A). Spontaneous process is an irreversible process and may ...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion (A). A liquid crystallises into a solid and is accompanied b...
Text Solution
|
- Derive the relationship between Delta H " and " Delta U for an ideal g...
Text Solution
|
- Extensive properties depends on the quantity of matter but intensive p...
Text Solution
|
- The lattice enthalpy of an ionic compound is the enthalpy when one mol...
Text Solution
|
- Delta G is energy availabe to do useful work and is thus a meaure of "...
Text Solution
|
- Graphically shoe the total work done in an expansion when the state of...
Text Solution
|