Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT EXEMPLAR-ANATOMY OF FLOWERING PLANTS-Long Answer
- The arrangement of ovules within the ovary is known as placentation. W...
Text Solution
|
- Deciduous plants shed their leaves during hot summer of in autumn. Thi...
Text Solution
|
- Is Pinus an evergreen tree ? Comment.
Text Solution
|
- Assume that a pencil box held in your hand, represents a plant cell. I...
Text Solution
|
- Each of the following terms has some anatomical signicance. What do th...
Text Solution
|
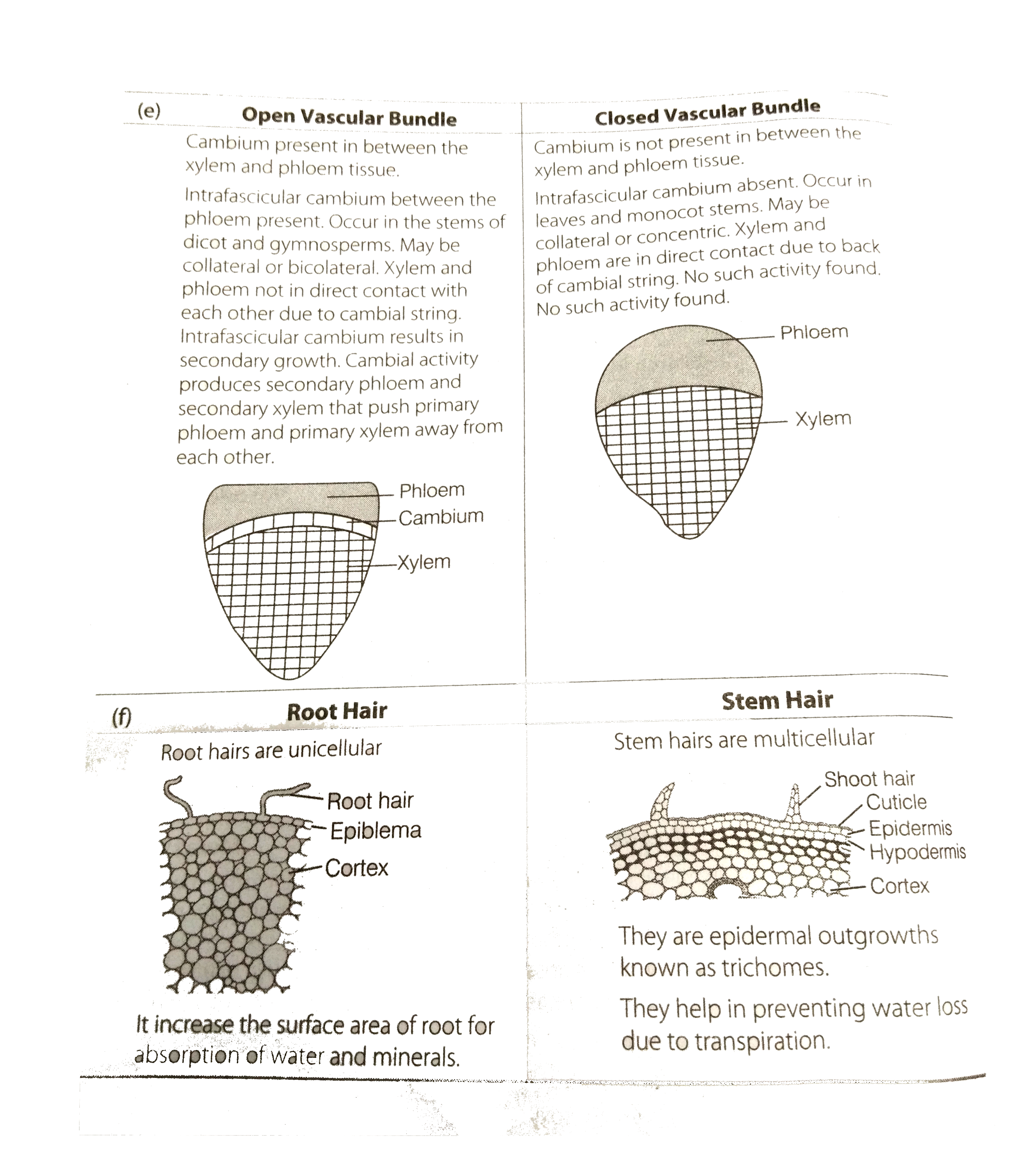
- Distinguish between the following (a) Exarch and endarch condition o...
Text Solution
|