Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT EXEMPLAR-TRANSPORT IN PLANTS-Short Answer Type Questions
- How is it that the intracellular level of K^(+) are higher than extrac...
Text Solution
|
- Cut pieces of beetroot do not leave the colour in cold water but do so...
Text Solution
|
- In a girdled plant, when water is supplied to the leaves above the gir...
Text Solution
|
- Varous types of transport mechanisms are needed to fulfil the mineral ...
Text Solution
|
- How can plants be grown limited water supply without compromising on m...
Text Solution
|
- Will the ascent of sap be possible without the cohesion and adhesion o...
Text Solution
|
- Keep some freshly cut flowers in a solution of food colour. Wait for s...
Text Solution
|
- When a freshly collected Spirogyra filament is kept in a 10 % potassiu...
Text Solution
|
- Sugar crystals do not dissolve easily in ice cold water. Explain.
Text Solution
|
- Salt is applied to tennis lawns to kill weeds. How does salting tennis...
Text Solution
|
- What is the chemical composition of of xylem and phloem sap ?
Text Solution
|
- If you are provided with two tubes (A and B), where one is narrow and ...
Text Solution
|
- What are 'aquaporins' ? How does presence of aquaporins affect osmosis...
Text Solution
|
- ABA (Abscisic Acid) is called a stress hormone. A. How this hormone ...
Text Solution
|
- We know that plants are harmed by excess water. But plants survive und...
Text Solution
|
- Differentiate between diffusion and translocation in plants.
Text Solution
|
- How is fcilitated diffusion different from diffusion ?
Text Solution
|
- Explain the mass flow hypothesis of transport in phloem.
Text Solution
|
- Observe the diagram and answer the following. (a) Are these types...
Text Solution
|
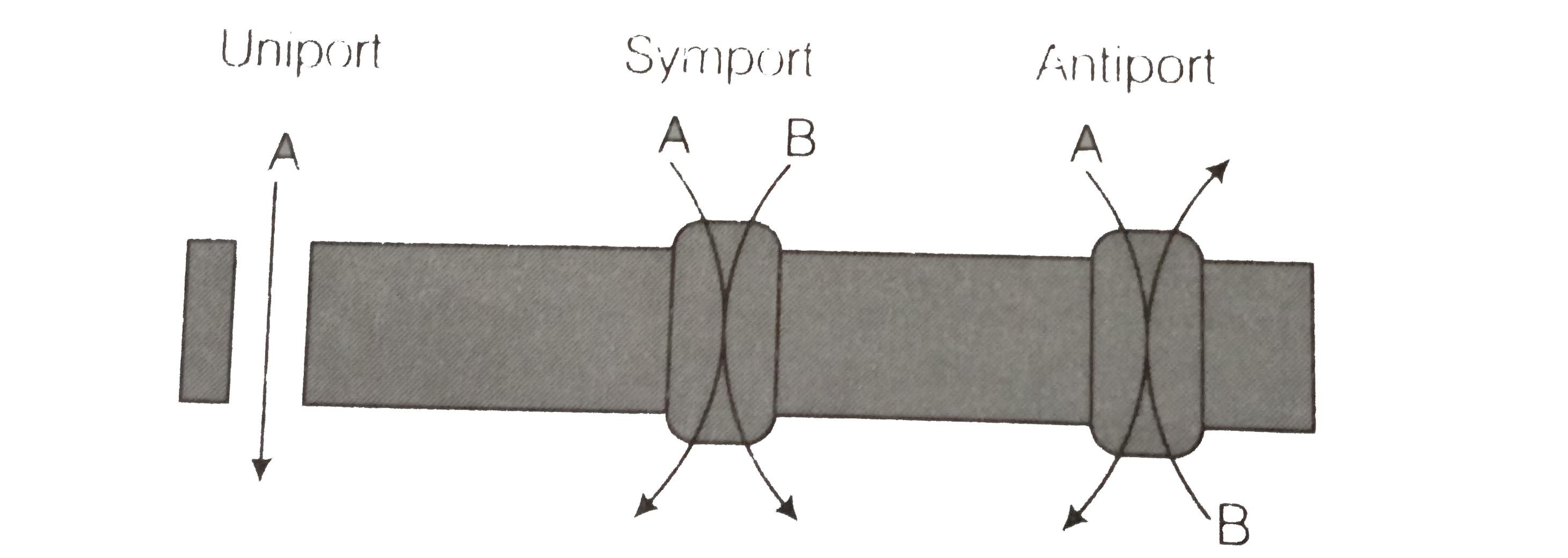
- Define uniport, symport and antiport. Do they require energy ?
Text Solution
|