Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
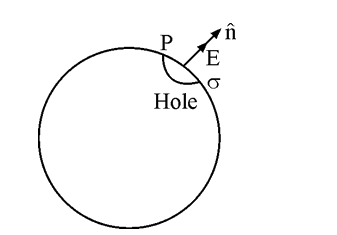
- A hollow charged conductor has a tiny hole cut into its surface. Sho...
Text Solution
|
- A hollow charged conductor has a tiny hole cut into its surface. Sho...
Text Solution
|
- Show that the normal component of electrostatic field has a discont...
Text Solution
|
- किसी खोखले आवेशित चालक में उसके पृष्ठ पर कोई छिन्द्र बनाया गया है । यह...
Text Solution
|
- एक खोखले आवेशित गोले की सतह पर एक छोटा छिद्र काटा गया है। सिद्ध करो की...
Text Solution
|
- A hollow charged conductor has a tiny hole cut into its surface. Show ...
Text Solution
|
- A hollow charged conductor has a tiny hole cut into its surface. Show ...
Text Solution
|
- A hollow charged conductor has a tiny hole cut into its surface. Sho...
Text Solution
|
- A hollow charged conductor has a tiny hole cut in to its surface show ...
Text Solution
|