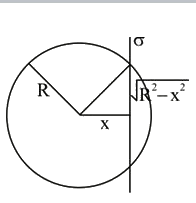
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- An infinite, uniformly charged sheet with surface charge density sigma...
Text Solution
|
- An infinite, uniformly charged sheet with surface charge density sigma...
Text Solution
|
- A charge Q is enclosed by a spherical Gaussian surface of radius R. I...
Text Solution
|
- A charge of 8.85C is placed at the centre of a spherical Gaussian surf...
Text Solution
|
- Four Gaussian surface are given below with charges inside each Gaussia...
Text Solution
|
- Four Gaussian surface are given below with charges inside each Gaussia...
Text Solution
|
- An infinite, uniformly charged sheet with surface density sigma cuts t...
Text Solution
|
- An infinite uniformly charged sheet with surface charge densitysigma...
Text Solution
|
- R is uniformly charged at a distance x from the center of a spherical ...
Text Solution
|